上一节我们分析到了Execution的生成,然后调用taskManagerGateway.submitTask方法提交task,提交的时候会将executionVertex封装成TaskDeploymentDescriptor,task的提交与执行涉及到了flink多个组件的配合,之前没有详细讲过,可能有的小伙伴有点不太清楚,这里我们花点时间介绍一下。
1.Flink各个组件介绍
1.JobManager
在JobManager启动的时候会启动三个比较重要的组件:
1. WebMonitorEndpoint: 里面有大约六七十个handler,如果客户端使用fink run的方式来提交一个job,最终会由WebMonitorEndpoint的submitJobHandler来处理。
2. Dispatcher: 负责接收用户提交的jobGraph,然后启动Jobmaster。
3. ResourceManager: Flink集群的资源管理器,关于slot的管理和申请工作都由他负责。
2.TaskManager
TaskManager:是flink的worker节点,它是负责flink中本机slot资源的管理以及task的执行。TaskManager上基本的资源单位时slot,一个作业的task最终会在TaskManager上的slot上运行,TaskManager负责维护本地的slot资源列表,并和jobMaster进行通信。
2.TaskExecutor#submitTask
上节我们在execution中看到它调用了taskManagerGateway.submitTask方法提交task,taskManagerGateway是一个接口,我们点进它的子类RpcTaskManagerGateway中可以看到它调用了TaskExecutorGateway的submitTask方法。
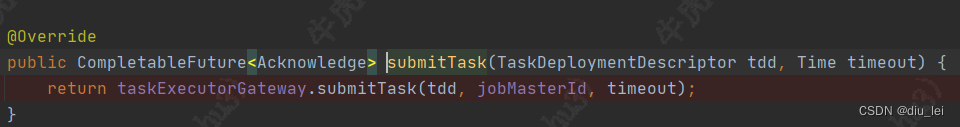
TaskExecutorGateway也是一个接口,我们可以点进它的子类TaskExecutor,然后我们找到他的submitTask方法
@Override
public CompletableFuture submitTask(
TaskDeploymentDescriptor tdd,
JobMasterId jobMasterId,
Time timeout) {
try {
//获取jobid和尝试次数id
final JobID jobId = tdd.getJobId();
final ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID = tdd.getExecutionAttemptId();
//获取jobmanager的连接
final JobTable.Connection jobManagerConnection = jobTable.getConnection(jobId).orElseThrow(() -> {
final String message = "Could not submit task because there is no JobManager " +
"associated for the job " + jobId + '.';
log.debug(message);
return new TaskSubmissionException(message);
});
if (!Objects.equals(jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId(), jobMasterId)) {
final String message = "Rejecting the task submission because the job manager leader id " +
jobMasterId + " does not match the expected job manager leader id " +
jobManagerConnection.getJobMasterId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
if (!taskSlotTable.tryMarkSlotActive(jobId, tdd.getAllocationId())) {
final String message = "No task slot allocated for job ID " + jobId +
" and allocation ID " + tdd.getAllocationId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
// re-integrate offloaded data:
try {
tdd.loadBigData(blobCacheService.getPermanentBlobService());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not re-integrate offloaded TaskDeploymentDescriptor data.", e);
}
// deserialize the pre-serialized information
final JobInformation jobInformation;
final TaskInformation taskInformation;
try {
//反序列化获取task信息和Job信息
jobInformation = tdd.getSerializedJobInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
taskInformation = tdd.getSerializedTaskInformation().deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not deserialize the job or task information.", e);
}
if (!jobId.equals(jobInformation.getJobId())) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException(
"Inconsistent job ID information inside TaskDeploymentDescriptor (" +
tdd.getJobId() + " vs. " + jobInformation.getJobId() + ")");
}
//将task相关信息加入到taskMetricGroup
TaskMetricGroup taskMetricGroup = taskManagerMetricGroup.addTaskForJob(
jobInformation.getJobId(),
jobInformation.getJobName(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskInformation.getTaskName(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber());
InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider = new RpcInputSplitProvider(
jobManagerConnection.getJobManagerGateway(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
taskManagerConfiguration.getTimeout());
final TaskOperatorEventGateway taskOperatorEventGateway = new RpcTaskOperatorEventGateway(
jobManagerConnection.getJobManagerGateway(),
executionAttemptID,
(t) -> runAsync(() -> failTask(executionAttemptID, t)));
TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions = jobManagerConnection.getTaskManagerActions();
CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder = jobManagerConnection.getCheckpointResponder();
GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager = jobManagerConnection.getGlobalAggregateManager();
LibraryCacheManager.ClassLoaderHandle classLoaderHandle = jobManagerConnection.getClassLoaderHandle();
ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier = jobManagerConnection.getResultPartitionConsumableNotifier();
PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionStateChecker = jobManagerConnection.getPartitionStateChecker();
//本地状态存储
final TaskLocalStateStore localStateStore = localStateStoresManager.localStateStoreForSubtask(
jobId,
tdd.getAllocationId(),
taskInformation.getJobVertexId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex());
final JobManagerTaskRestore taskRestore = tdd.getTaskRestore();
final TaskStateManager taskStateManager = new TaskStateManagerImpl(
jobId,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
localStateStore,
taskRestore,
checkpointResponder);
MemoryManager memoryManager;
try {
memoryManager = taskSlotTable.getTaskMemoryManager(tdd.getAllocationId());
} catch (SlotNotFoundException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not submit task.", e);
}
//在实例化方法中构造InputGate和ResultPartition
Task task = new Task(
jobInformation,
taskInformation,
tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(),
tdd.getAllocationId(),
tdd.getSubtaskIndex(),
tdd.getAttemptNumber(),
tdd.getProducedPartitions(),
tdd.getInputGates(),
tdd.getTargetSlotNumber(),
memoryManager,
taskExecutorServices.getIOManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getShuffleEnvironment(),
taskExecutorServices.getKvStateService(),
taskExecutorServices.getBroadcastVariableManager(),
taskExecutorServices.getTaskEventDispatcher(),
externalResourceInfoProvider,
taskStateManager,
taskManagerActions,
inputSplitProvider,
checkpointResponder,
taskOperatorEventGateway,
aggregateManager,
classLoaderHandle,
fileCache,
taskManagerConfiguration,
taskMetricGroup,
resultPartitionConsumableNotifier,
partitionStateChecker,
getRpcService().getExecutor());
taskMetricGroup.gauge(MetricNames.IS_BACKPRESSURED, task::isBackPressured);
log.info("Received task {} ({}), deploy into slot with allocation id {}.",
task.getTaskInfo().getTaskNameWithSubtasks(), tdd.getExecutionAttemptId(), tdd.getAllocationId());
boolean taskAdded;
try {
taskAdded = taskSlotTable.addTask(task);
} catch (SlotNotFoundException | SlotNotActiveException e) {
throw new TaskSubmissionException("Could not submit task.", e);
}
if (taskAdded) {
task.startTaskThread();
setupResultPartitionBookkeeping(
tdd.getJobId(),
tdd.getProducedPartitions(),
task.getTerminationFuture());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());
} else {
final String message = "TaskManager already contains a task for id " +
task.getExecutionId() + '.';
log.debug(message);
throw new TaskSubmissionException(message);
}
} catch (TaskSubmissionException e) {
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(e);
}
}
这个方法体很长,里面做了很多工作,但其中最重要的有两部分:
1.Task的实例化,在task实例化的过程中创建了InputGate和ResultPartition
2.Task线程的启动,task线程启动后,会将inputGate和ResultPartition拉起来,使用inputGate接入数据,buffer pool用来缓存数据
3.Task的实例化
这个是task的构造方法,里面有很多东西,我们也不需要全都看懂,我们只要看对我们来说比较重要的就好了
public Task( JobInformation jobInformation, TaskInformation taskInformation, ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID, AllocationID slotAllocationId, int subtaskIndex, int attemptNumber, ListresultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors, List inputGateDeploymentDescriptors, int targetSlotNumber, MemoryManager memManager, IOManager ioManager, ShuffleEnvironment shuffleEnvironment, KvStateService kvStateService, BroadcastVariableManager bcVarManager, TaskEventDispatcher taskEventDispatcher, ExternalResourceInfoProvider externalResourceInfoProvider, TaskStateManager taskStateManager, TaskManagerActions taskManagerActions, InputSplitProvider inputSplitProvider, CheckpointResponder checkpointResponder, TaskOperatorEventGateway operatorCoordinatorEventGateway, GlobalAggregateManager aggregateManager, LibraryCacheManager.ClassLoaderHandle classLoaderHandle, FileCache fileCache, TaskManagerRuntimeInfo taskManagerConfig, @Nonnull TaskMetricGroup metricGroup, ResultPartitionConsumableNotifier resultPartitionConsumableNotifier, PartitionProducerStateChecker partitionProducerStateChecker, Executor executor) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobInformation); Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskInformation); Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= subtaskIndex, "The subtask index must be positive."); Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= attemptNumber, "The attempt number must be positive."); Preconditions.checkArgument(0 <= targetSlotNumber, "The target slot number must be positive."); this.taskInfo = new TaskInfo( taskInformation.getTaskName(), taskInformation.getMaxNumberOfSubtasks(), subtaskIndex, taskInformation.getNumberOfSubtasks(), attemptNumber, String.valueOf(slotAllocationId)); this.jobId = jobInformation.getJobId(); this.vertexId = taskInformation.getJobVertexId(); this.executionId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executionAttemptID); this.allocationId = Preconditions.checkNotNull(slotAllocationId); this.taskNameWithSubtask = taskInfo.getTaskNameWithSubtasks(); this.jobConfiguration = jobInformation.getJobConfiguration(); this.taskConfiguration = taskInformation.getTaskConfiguration(); this.requiredJarFiles = jobInformation.getRequiredJarFileBlobKeys(); this.requiredClasspaths = jobInformation.getRequiredClasspathURLs(); this.nameOfInvokableClass = taskInformation.getInvokableClassName(); this.serializedExecutionConfig = jobInformation.getSerializedExecutionConfig(); Configuration tmConfig = taskManagerConfig.getConfiguration(); this.taskCancellationInterval = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_INTERVAL); this.taskCancellationTimeout = tmConfig.getLong(TaskManagerOptions.TASK_CANCELLATION_TIMEOUT); this.memoryManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(memManager); this.ioManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(ioManager); this.broadcastVariableManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(bcVarManager); this.taskEventDispatcher = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskEventDispatcher); this.taskStateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskStateManager); this.accumulatorRegistry = new AccumulatorRegistry(jobId, executionId); this.inputSplitProvider = Preconditions.checkNotNull(inputSplitProvider); this.checkpointResponder = Preconditions.checkNotNull(checkpointResponder); this.operatorCoordinatorEventGateway = Preconditions.checkNotNull(operatorCoordinatorEventGateway); this.aggregateManager = Preconditions.checkNotNull(aggregateManager); this.taskManagerActions = checkNotNull(taskManagerActions); this.externalResourceInfoProvider = checkNotNull(externalResourceInfoProvider); this.classLoaderHandle = Preconditions.checkNotNull(classLoaderHandle); this.fileCache = Preconditions.checkNotNull(fileCache); this.kvStateService = Preconditions.checkNotNull(kvStateService); this.taskManagerConfig = Preconditions.checkNotNull(taskManagerConfig); this.metrics = metricGroup; this.partitionProducerStateChecker = Preconditions.checkNotNull(partitionProducerStateChecker); this.executor = Preconditions.checkNotNull(executor); // create the reader and writer structures final String taskNameWithSubtaskAndId = taskNameWithSubtask + " (" + executionId + ')'; final ShuffleIOOwnerContext taskShuffleContext = shuffleEnvironment .createShuffleIOOwnerContext(taskNameWithSubtaskAndId, executionId, metrics.getIOMetricGroup()); // produced intermediate result partitions //创建ResultPartitionWriter final ResultPartitionWriter[] resultPartitionWriters = shuffleEnvironment.createResultPartitionWriters( taskShuffleContext, resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors).toArray(new ResultPartitionWriter[] {}); this.consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters = ConsumableNotifyingResultPartitionWriterDecorator.decorate( resultPartitionDeploymentDescriptors, resultPartitionWriters, this, jobId, resultPartitionConsumableNotifier); // consumed intermediate result partitions //创建inputGate final IndexedInputGate[] gates = shuffleEnvironment.createInputGates( taskShuffleContext, this, inputGateDeploymentDescriptors) .toArray(new IndexedInputGate[0]); this.inputGates = new IndexedInputGate[gates.length]; int counter = 0; for (IndexedInputGate gate : gates) { inputGates[counter++] = new InputGateWithMetrics(gate, metrics.getIOMetricGroup().getNumBytesInCounter()); } if (shuffleEnvironment instanceof NettyShuffleEnvironment) { //noinspection deprecation ((NettyShuffleEnvironment) shuffleEnvironment) .registerLegacyNetworkMetrics(metrics.getIOMetricGroup(), resultPartitionWriters, gates); } invokableHasBeenCanceled = new AtomicBoolean(false); // finally, create the executing thread, but do not start it executingThread = new Thread(TASK_THREADS_GROUP, this, taskNameWithSubtask); }
这个方法体里面有3个部分比较重要:
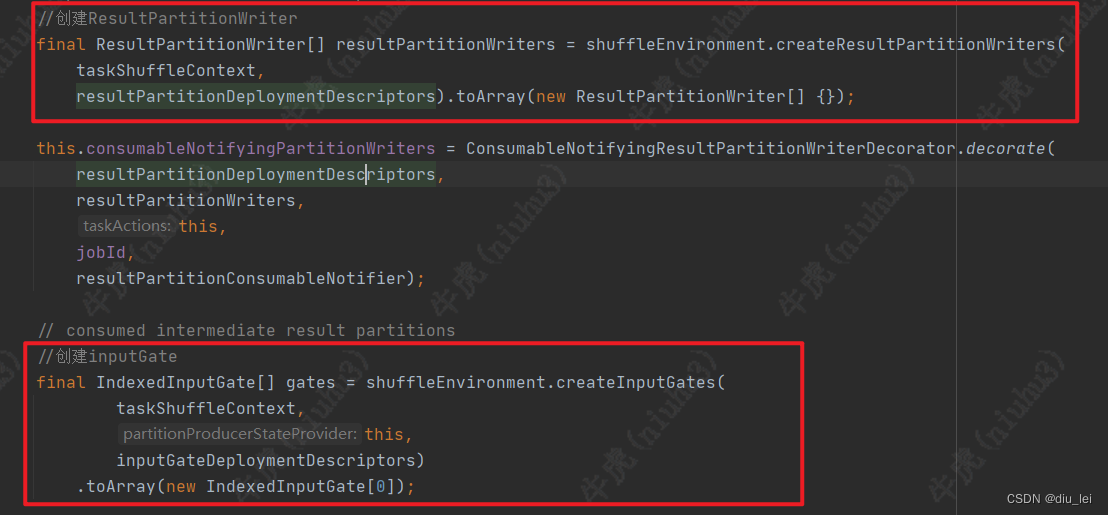
1.ResultPartitionWriter和InputGate的创建
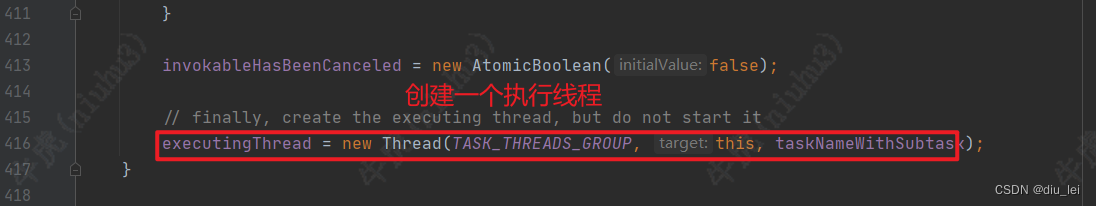
2.创建一个执行线程,后面启动的task线程就是这个
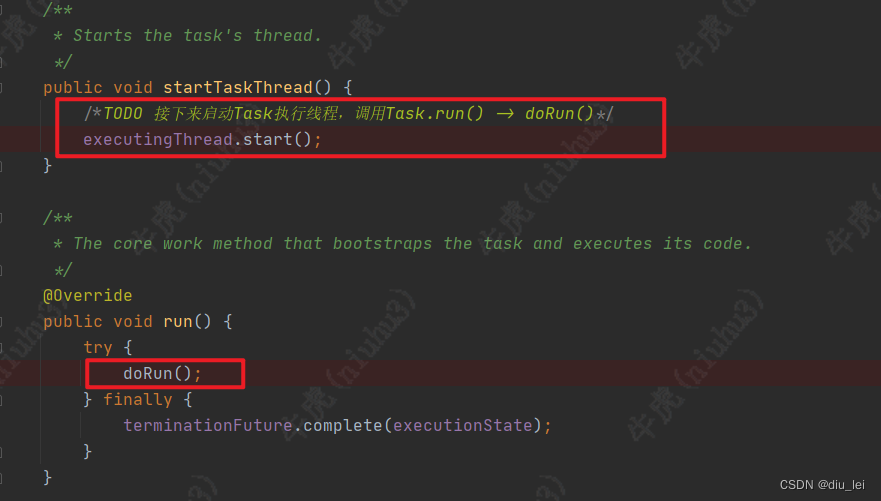
4.Task线程的启动
task线程启动后会去调用自己的run方法,我们再run方法中可以看到run方法又调用了doRun方法
doRun方法的方法体也是很长,我们还是只找重点,前面无非就是变更状态
private void doRun() {
// ----------------------------
// Initial State transition
// ----------------------------
while (true) {
ExecutionState current = this.executionState;
if (current == ExecutionState.CREATED) {
if (transitionState(ExecutionState.CREATED, ExecutionState.DEPLOYING)) {
// success, we can start our work
break;
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.FAILED) {
// we were immediately failed. tell the TaskManager that we reached our final state
notifyFinalState();
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
return;
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.CANCELING) {
if (transitionState(ExecutionState.CANCELING, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
// we were immediately canceled. tell the TaskManager that we reached our final state
notifyFinalState();
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
return;
}
}
else {
if (metrics != null) {
metrics.close();
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid state for beginning of operation of task " + this + '.');
}
}
// all resource acquisitions and registrations from here on
// need to be undone in the end
Map> distributedCacheEntries = new HashMap<>();
AbstractInvokable invokable = null;
try {
// ----------------------------
// Task Bootstrap - We periodically
// check for canceling as a shortcut
// ----------------------------
// activate safety net for task thread
LOG.debug("Creating FileSystem stream leak safety net for task {}", this);
FileSystemSafetyNet.initializeSafetyNetForThread();
// first of all, get a user-code classloader
// this may involve downloading the job's JAR files and/or classes
LOG.info("Loading JAR files for task {}.", this);
userCodeClassLoader = createUserCodeClassloader();
final ExecutionConfig executionConfig = serializedExecutionConfig.deserializeValue(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
if (executionConfig.getTaskCancellationInterval() >= 0) {
// override task cancellation interval from Flink config if set in ExecutionConfig
taskCancellationInterval = executionConfig.getTaskCancellationInterval();
}
if (executionConfig.getTaskCancellationTimeout() >= 0) {
// override task cancellation timeout from Flink config if set in ExecutionConfig
taskCancellationTimeout = executionConfig.getTaskCancellationTimeout();
}
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// register the task with the network stack
// this operation may fail if the system does not have enough
// memory to run the necessary data exchanges
// the registration must also strictly be undone
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
LOG.info("Registering task at network: {}.", this);
//设置resultPartition和inputGate
setupPartitionsAndGates(consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters, inputGates);
for (ResultPartitionWriter partitionWriter : consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters) {
taskEventDispatcher.registerPartition(partitionWriter.getPartitionId());
}
// next, kick off the background copying of files for the distributed cache
try {
for (Map.Entry entry :
DistributedCache.readFileInfoFromConfig(jobConfiguration)) {
LOG.info("Obtaining local cache file for '{}'.", entry.getKey());
Future cp = fileCache.createTmpFile(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), jobId, executionId);
distributedCacheEntries.put(entry.getKey(), cp);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(
String.format("Exception while adding files to distributed cache of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId), e);
}
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// call the user code initialization methods
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
TaskKvStateRegistry kvStateRegistry = kvStateService.createKvStateTaskRegistry(jobId, getJobVertexId());
Environment env = new RuntimeEnvironment(
jobId,
vertexId,
executionId,
executionConfig,
taskInfo,
jobConfiguration,
taskConfiguration,
userCodeClassLoader,
memoryManager,
ioManager,
broadcastVariableManager,
taskStateManager,
aggregateManager,
accumulatorRegistry,
kvStateRegistry,
inputSplitProvider,
distributedCacheEntries,
consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters,
inputGates,
taskEventDispatcher,
checkpointResponder,
operatorCoordinatorEventGateway,
taskManagerConfig,
metrics,
this,
externalResourceInfoProvider);
// Make sure the user code classloader is accessible thread-locally.
// We are setting the correct context class loader before instantiating the invokable
// so that it is available to the invokable during its entire lifetime.
executingThread.setContextClassLoader(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
// now load and instantiate the task's invokable code
/*TODO 加载和实例化task的可执行代码*/
invokable = loadAndInstantiateInvokable(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader(), nameOfInvokableClass, env);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// actual task core work
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// we must make strictly sure that the invokable is accessible to the cancel() call
// by the time we switched to running.
this.invokable = invokable;
// switch to the RUNNING state, if that fails, we have been canceled/failed in the meantime
if (!transitionState(ExecutionState.DEPLOYING, ExecutionState.RUNNING)) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// notify everyone that we switched to running
taskManagerActions.updateTaskExecutionState(new TaskExecutionState(jobId, executionId, ExecutionState.RUNNING));
// make sure the user code classloader is accessible thread-locally
executingThread.setContextClassLoader(userCodeClassLoader.asClassLoader());
// run the invokable
/*TODO 执行代码( invokable即为operator对象实例,比如 StreamTask里)*/
invokable.invoke();
// make sure, we enter the catch block if the task leaves the invoke() method due
// to the fact that it has been canceled
if (isCanceledOrFailed()) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// finalization of a successful execution
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// finish the produced partitions. if this fails, we consider the execution failed.
for (ResultPartitionWriter partitionWriter : consumableNotifyingPartitionWriters) {
if (partitionWriter != null) {
partitionWriter.finish();
}
}
// try to mark the task as finished
// if that fails, the task was canceled/failed in the meantime
if (!transitionState(ExecutionState.RUNNING, ExecutionState.FINISHED)) {
throw new CancelTaskException();
}
}
catch (Throwable t) {
// unwrap wrapped exceptions to make stack traces more compact
if (t instanceof WrappingRuntimeException) {
t = ((WrappingRuntimeException) t).unwrap();
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// the execution failed. either the invokable code properly failed, or
// an exception was thrown as a side effect of cancelling
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
TaskManagerExceptionUtils.tryEnrichTaskManagerError(t);
try {
// check if the exception is unrecoverable
if (ExceptionUtils.isJvmFatalError(t) ||
(t instanceof OutOfMemoryError && taskManagerConfig.shouldExitJvmOnOutOfMemoryError())) {
// terminate the JVM immediately
// don't attempt a clean shutdown, because we cannot expect the clean shutdown to complete
try {
LOG.error("Encountered fatal error {} - terminating the JVM", t.getClass().getName(), t);
} finally {
Runtime.getRuntime().halt(-1);
}
}
// transition into our final state. we should be either in DEPLOYING, RUNNING, CANCELING, or FAILED
// loop for multiple retries during concurrent state changes via calls to cancel() or
// to failExternally()
while (true) {
ExecutionState current = this.executionState;
if (current == ExecutionState.RUNNING || current == ExecutionState.DEPLOYING) {
if (t instanceof CancelTaskException) {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
cancelInvokable(invokable);
break;
}
}
else {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.FAILED, t)) {
// proper failure of the task. record the exception as the root cause
failureCause = t;
cancelInvokable(invokable);
break;
}
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.CANCELING) {
if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.CANCELED)) {
break;
}
}
else if (current == ExecutionState.FAILED) {
// in state failed already, no transition necessary any more
break;
}
// unexpected state, go to failed
else if (transitionState(current, ExecutionState.FAILED, t)) {
LOG.error("Unexpected state in task {} ({}) during an exception: {}.", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId, current);
break;
}
// else fall through the loop and
}
}
catch (Throwable tt) {
String message = String.format("FATAL - exception in exception handler of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
LOG.error(message, tt);
notifyFatalError(message, tt);
}
}
finally {
try {
LOG.info("Freeing task resources for {} ({}).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
// clear the reference to the invokable. this helps guard against holding references
// to the invokable and its structures in cases where this Task object is still referenced
this.invokable = null;
// free the network resources
releaseResources();
// free memory resources
if (invokable != null) {
memoryManager.releaseAll(invokable);
}
// remove all of the tasks resources
fileCache.releaseJob(jobId, executionId);
// close and de-activate safety net for task thread
LOG.debug("Ensuring all FileSystem streams are closed for task {}", this);
FileSystemSafetyNet.closeSafetyNetAndGuardedResourcesForThread();
notifyFinalState();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
// an error in the resource cleanup is fatal
String message = String.format("FATAL - exception in resource cleanup of task %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId);
LOG.error(message, t);
notifyFatalError(message, t);
}
// un-register the metrics at the end so that the task may already be
// counted as finished when this happens
// errors here will only be logged
try {
metrics.close();
}
catch (Throwable t) {
LOG.error("Error during metrics de-registration of task {} ({}).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId, t);
}
}
}
638行有一句代码比较重要,就是拉起我们之前创建的InputGate和ResultPartition
这些准备工作做好之后,就是开始加载和实例化task的可执行代码
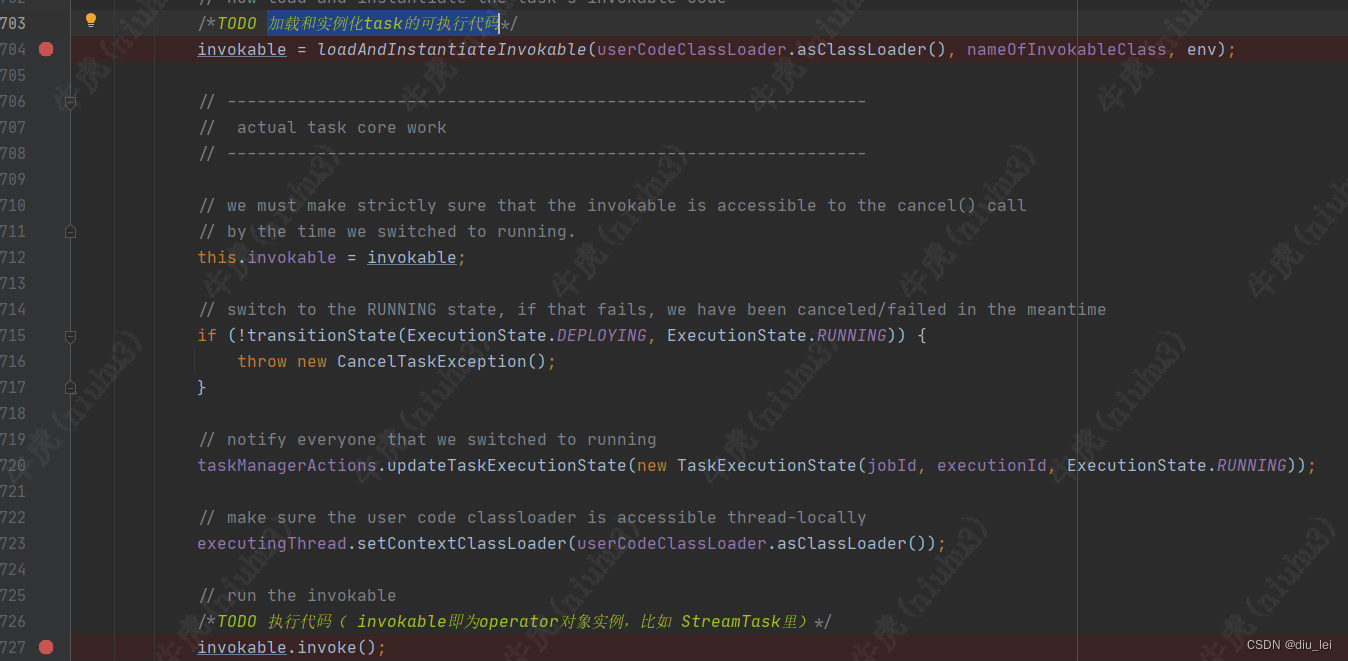
上面代码调用了loadAndInstantiateInvokable方法,在这个方法中利用反射获取他的构造方法并创建实例,到这里可能有的兄弟就有点晕了,不知道接下来该往哪里跳了
private static AbstractInvokable loadAndInstantiateInvokable(
ClassLoader classLoader,
String className,
Environment environment) throws Throwable {
final Class invokableClass;
try {
//反射获取主类
invokableClass = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader)
.asSubclass(AbstractInvokable.class);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new Exception("Could not load the task's invokable class.", t);
}
Constructor statelessCtor;
try {
//获取该反射类的构造方法
statelessCtor = invokableClass.getConstructor(Environment.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ee) {
throw new FlinkException("Task misses proper constructor", ee);
}
// instantiate the class
try {
//noinspection ConstantConditions --> cannot happen
//实例化构造方法
return statelessCtor.newInstance(environment);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// directly forward exceptions from the eager initialization
throw e.getTargetException();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FlinkException("Could not instantiate the task's invokable class.", e);
}
}
其实在构建StreamGraph的时候就指定了invokableClass ,在生成 StreamNode 的时候,会通过
OpearatorFactory 执行判断,如果该 StreamOperator 是 StreamSource 的话,就会指定该 StreamTask 的 invokableClass 为 SourceStreamTask , 否则为 ( OneInputStreamTask , TwoInputStreamTask , StreamTask )。核心代码是:StreamGraph.addOperator(....){
invokableClass = operatorFactory.isStreamSource() ? SourceStreamTask.class :
OneInputStreamTask.class;
}
后面我们就可以根据具体的task类型点进对应的构造方法中去看对应的实际逻辑。
猜你喜欢
网友评论
- 搜索
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
