一、ArkTS语言基本语法
1.简介
HarmonyOS的ArkTS语言是一种基于TypeScript开发的语言,它专为HarmonyOS系统开发而设计。ArkTS语言结合了JavaScript的灵活性和TypeScript的严谨性,使得开发者能够快速、高效地开发出高质量的HarmonyOS应用程序。
ArkTS语言具有以下特点:
-
静态类型检查:开发者在编写代码时可以使用类型注解来进行类型检查,从而减少因类型错误而导致的bug。
-
异步/同步编程:ArkTS语言支持基于Promise和async/await的异步/同步编程方式,能够更好地处理异步操作。
-
内置模块:ArkTS语言内置了许多常用的模块,如文件系统、网络请求、图形渲染等,使得开发者不必自己编写这些模块。
-
兼容性:ArkTS语言使用TypeScript语法,可以与JavaScript代码无缝集成,并且可以编译成JavaScript代码来在其他平台上运行。
ArkTS语言基础类库是HarmonyOS系统上为应用开发者提供的常用基础能力,主要包含能力如下图所示:

ArkTS是HarmonyOS优选的主力应用开发语言。ArkTS围绕应用开发在TypeScript(简称TS)生态基础上做了进一步扩展,继承了TS的所有特性,是TS的超集。
ArkTS和HTML的差别: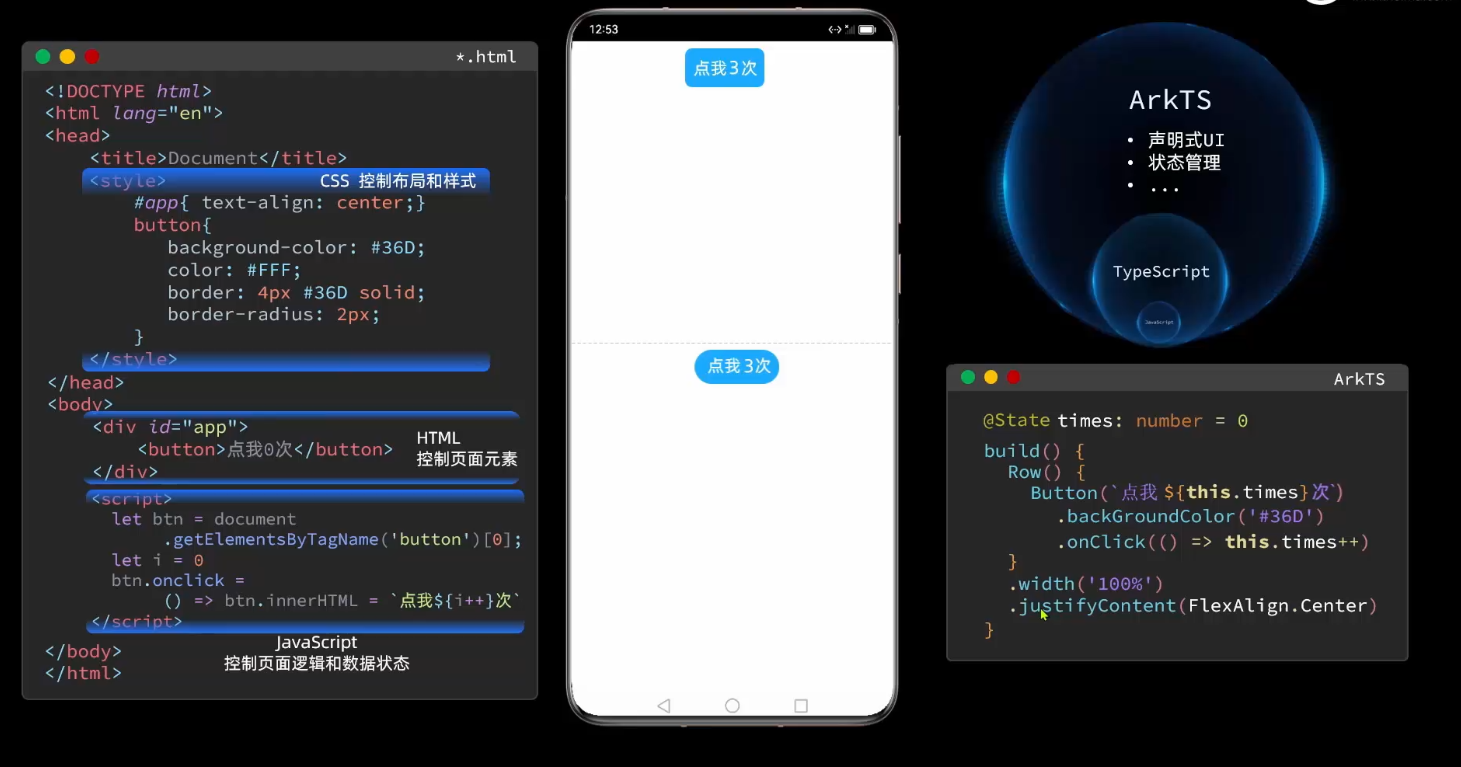

2.TypeScript的基础语法
TypeScript是一种由微软开发的JavaScript超集语言,它支持JavaScript的所有语法,但添加了一些新的特性和语法,使开发更加可靠和高效。TypeScript最大的特点是引入了静态类型,开发者可以在编译时发现类型错误,提高代码的可维护性和可读性。
TypeScript代码可以在编译时被转换成JavaScript代码,在浏览器和Node.js环境下都可以运行。虽然TypeScript相对于JavaScript来说更加复杂,但是它可以帮助开发者更好地组织和管理复杂的项目,特别是在团队协作中提高代码的质量和可维护性。
TypeScript基础知识包括基本类型、变量声明、函数、类、接口、泛型等。另外,TypeScript还支持模块化开发,可以使用ES模块规范或者CommonJS规范导入和导出模块。在实际项目开发中,TypeScript还可以结合工具链如Webpack、Babel进行编译、打包等操作。
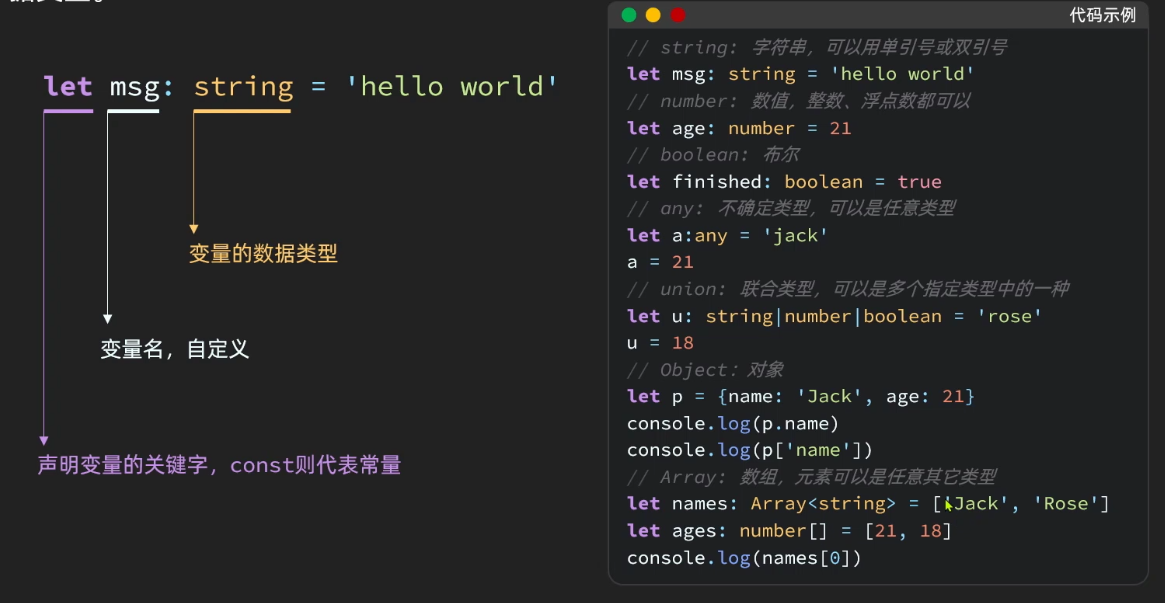
除了上面提到的变量声明、函数定义、类定义、接口定义和枚举类型外,TypeScript还有一些基础语法需要掌握:
2.1 类型注解
TypeScript的静态类型检查是通过类型注解实现的。在声明变量或函数时,可以使用冒号加上类型注解,指定变量或函数的类型。例如:
let name: string = "TypeScript";
function add(a: number, b: number): number {
return a + b;
}
2.2 接口
TypeScript的接口是用来描述对象的形状的。可以定义对象需要包含哪些属性和方法,以及它们的类型。例如:
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
sayHello(): void;
}
let tom: Person = {
name: "Tom",
age: 18,
sayHello: function() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name}!`);
}
};
2.3 泛型
TypeScript的泛型可以帮助我们编写更加灵活、可重用的代码。它允许在编写函数、类或接口时使用参数化类型,从而提高代码的通用性和可读性。例如:
function identity(arg: T): T { return arg; } let output = identity ("TypeScript"); console.log(output); // 输出 TypeScript
2.4 类的继承
TypeScript的类可以继承其他类,从而实现代码的重用和扩展。通过关键字extends可以让一个类继承另一个类,并继承其属性和方法。例如:
class Animal {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
move(distance: number = 0) {
console.log(`${this.name} moved ${distance}m.`);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
bark() {
console.log("Woof! Woof!");
}
}
let dog = new Dog("Bobby");
dog.move(10); // 输出 "Bobby moved 10m."
dog.bark(); // 输出 "Woof! Woof!"
2.5 类的访问修饰符
TypeScript的类可以通过访问修饰符来控制类的属性和方法的访问权限。有三个访问修饰符可以使用:public、private和protected。默认情况下,都是public。
public:公共的,任何外部或内部都可以访问。
private:私有的,只有类的内部可以访问,外部无法访问。
protected:受保护的,只有类的内部和其子类可以访问,外部无法访问。
class Person {
protected name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
protected sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}.`);
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name: string) {
super(name);
}
public sayHelloToTeacher(teacher: Person) {
console.log(`Hello, ${teacher.name}, I'm ${this.name}.`);
}
}
let tom = new Student("Tom");
let bob = new Person("Bob");
tom.sayHelloToTeacher(bob); // 输出 "Hello, Bob, I'm Tom."
bob.sayHello(); // 报错:属性 'sayHello' 受保护,只能在类 'Person' 及其子类中访问。
以上只是举例一些TS的基础语法,TS内容远不止这些不懂的可以去学学TS。
3.ArkTS的基本组成
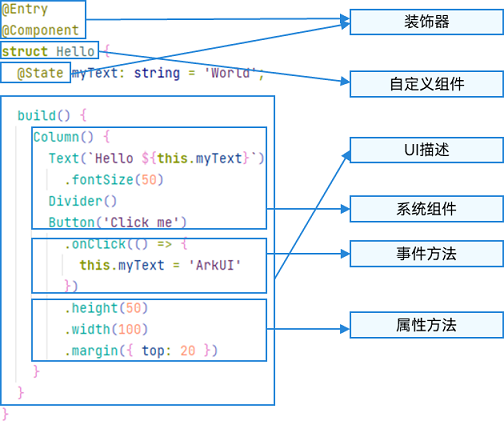
-
装饰器:用于装饰类、结构、方法以及变量,并赋予其特殊的含义。如上述示例中@Entry、@Component和@State都是装饰器,@Component表示自定义组件,@Entry表示该自定义组件为入口组件,@State表示组件中的状态变量,状态变量变化会触发UI刷新。
-
UI描述:以声明式的方式来描述UI的结构,例如build()方法中的代码块。
-
自定义组件:可复用的UI单元,可组合其他组件,如上述被@Component装饰的struct Hello。
-
系统组件:ArkUI框架中默认内置的基础和容器组件,可直接被开发者调用,比如示例中的Column、Text、Divider、Button。
-
属性方法:组件可以通过链式调用配置多项属性,如fontSize()、width()、height()、backgroundColor()等。
-
事件方法:组件可以通过链式调用设置多个事件的响应逻辑,如跟随在Button后面的onClick()。
系统组件、属性方法、事件方法具体使用可参考基于ArkTS的声明式开发范式。
除此之外,ArkTS扩展了多种语法范式来使开发更加便捷:
- @Builder/@BuilderParam:特殊的封装UI描述的方法,细粒度的封装和复用UI描述。
- @Extend/@Style:扩展内置组件和封装属性样式,更灵活地组合内置组件。
- stateStyles:多态样式,可以依据组件的内部状态的不同,设置不同样式。
4.自定义组件
@Component struct HelloComponent { @State message: string = 'Hello, World!'; build() { // HelloComponent自定义组件组合系统组件Row和Text Row() { Text(this.message) .onClick(() => { // 状态变量message的改变驱动UI刷新,UI从'Hello, World!'刷新为'Hello, ArkUI!' this.message = 'Hello, ArkUI!'; }) } } } @Entry @Component struct ParentComponent { build() { Column() { Text('ArkUI message') HelloComponent({ message: 'Hello, World!' }); Divider() HelloComponent({ message: '你好!' }); } } }-
struct:自定义组件基于struct实现,struct + 自定义组件名 +
{…}的组合构成自定义组件,不能有继承关系。对于struct的实例化,可以省略new。
-
build()函数:build()函数用于定义自定义组件的声明式UI描述,自定义组件必须定义build()函数。
-
@Entry:@Entry装饰的自定义组件将作为UI页面的入口。在单个UI页面中,最多可以使用@Entry装饰一个自定义组件。@Entry可以接受一个可选的LocalStorage的参数。
4.1 build()函数规范
1、根节点唯一
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { build() { // 根节点唯一且必要,必须为容器组件 Row() { ChildComponent() } } } @Component struct ChildComponent { build() { // 根节点唯一且必要,可为非容器组件 Image('test.jpg') } }2、不允许声明本地变量、打印、作用域
build() { // 反例:不允许声明本地变量 let a: number = 1; // 反例:不允许console.info console.info('print debug log'); // 反例:不允许本地作用域 { ... } }3、不允许调用没有用@Builder装饰的方法,允许系统组件的参数是TS方法的返回值。
@Component struct ParentComponent { doSomeCalculations() { } calcTextValue(): string { return 'Hello World'; } @Builder doSomeRender() { Text(`Hello World`) } build() { Column() { // 反例:不能调用没有用@Builder装饰的方法 this.doSomeCalculations(); // 正例:可以调用 this.doSomeRender(); // 正例:参数可以为调用TS方法的返回值 Text(this.calcTextValue()) } } }4、不允许switch和表达式
build() { Column() { // 反例:不允许使用switch语法 switch (expression) { case 1: Text('...') break; case 2: Image('...') break; default: Text('...') break; } // 反例:不允许使用表达式 (this.aVar > 10) ? Text('...') : Image('...') } }5.页面和自定义组件生命周期
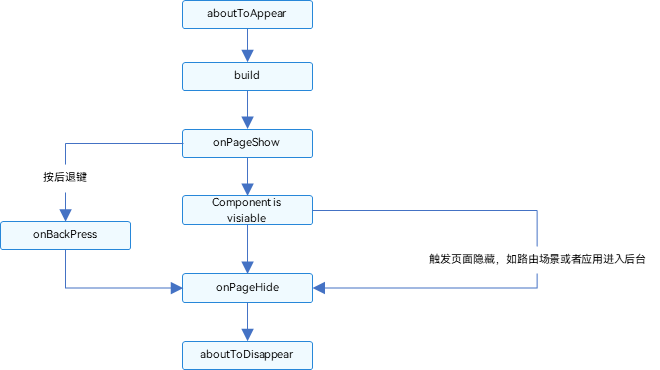
页面生命周期,即被@Entry装饰的组件生命周期,提供以下生命周期接口:
- onPageShow:页面每次显示时触发。
- onPageHide:页面每次隐藏时触发一次。
- onBackPress:当用户点击返回按钮时触发。
组件生命周期,即一般用@Component装饰的自定义组件的生命周期,提供以下生命周期接口:
- aboutToAppear:组件即将出现时回调该接口,具体时机为在创建自定义组件的新实例后,在执行其build()函数之前执行。
- aboutToDisappear:在自定义组件即将析构销毁时执行。
// Index.ets import router from '@ohos.router'; @Entry @Component struct MyComponent { @State showChild: boolean = true; // 只有被@Entry装饰的组件才可以调用页面的生命周期 onPageShow() { console.info('Index onPageShow'); } // 只有被@Entry装饰的组件才可以调用页面的生命周期 onPageHide() { console.info('Index onPageHide'); } // 只有被@Entry装饰的组件才可以调用页面的生命周期 onBackPress() { console.info('Index onBackPress'); } // 组件生命周期 aboutToAppear() { console.info('MyComponent aboutToAppear'); } // 组件生命周期 aboutToDisappear() { console.info('MyComponent aboutToDisappear'); } build() { Column() { // this.showChild为true,创建Child子组件,执行Child aboutToAppear if (this.showChild) { Child() } // this.showChild为false,删除Child子组件,执行Child aboutToDisappear Button('create or delete Child').onClick(() => { this.showChild = false; }) // push到Page2页面,执行onPageHide Button('push to next page') .onClick(() => { router.pushUrl({ url: 'pages/Page2' }); }) } } } @Component struct Child { @State title: string = 'Hello World'; // 组件生命周期 aboutToDisappear() { console.info('[lifeCycle] Child aboutToDisappear') } // 组件生命周期 aboutToAppear() { console.info('[lifeCycle] Child aboutToAppear') } build() { Text(this.title).fontSize(50).onClick(() => { this.title = 'Hello ArkUI'; }) } }6.装饰函数
6.1 @Builder装饰器
@Builder主要是定义页面UI
6.1.1 装饰指向
1、自定义组件内自定义构建函数
@Builder MyBuilderFunction(){ ... } #使用 this.MyBuilderFunction(){ ... }2、MyGlobalBuilderFunction()
@Builder function MyGlobalBuilderFunction(){ ... } #使用 MyGlobalBuilderFunction()6.1.2 参数传递
1、按引用传递参数
@Builder function ABuilder($$: { paramA1: string }) { Row() { Text(`UseStateVarByReference: ${$$.paramA1} `) } } @Entry @Component struct Parent { @State label: string = 'Hello'; build() { Column() { // 在Parent组件中调用ABuilder的时候,将this.label引用传递给ABuilder ABuilder({ paramA1: this.label }) Button('Click me').onClick(() => { // 点击“Click me”后,UI从“Hello”刷新为“ArkUI” this.label = 'ArkUI'; }) } } }2、按值传递参数
@Builder function ABuilder(paramA1: string) { Row() { Text(`UseStateVarByValue: ${paramA1} `) } } @Entry @Component struct Parent { label: string = 'Hello'; build() { Column() { ABuilder(this.label) } } }6.2 @BuilderParam装饰器
@BuilderParam用来装饰指向@Builder方法的变量,开发者可在初始化自定义组件时对此属性进行赋值,为自定义组件增加特定的功能。
6.2.1 装饰指向
1、本地初始化@BuilderParam
@Builder function GlobalBuilder0() {} @Component struct Child { @Builder doNothingBuilder() {}; @BuilderParam aBuilder0: () => void = this.doNothingBuilder; @BuilderParam aBuilder1: () => void = GlobalBuilder0; build(){} }2、初始化子组件@BuilderParam
@Component struct Child { @BuilderParam aBuilder0: () => void; build() { Column() { this.aBuilder0() } } } @Entry @Component struct Parent { @Builder componentBuilder() { Text(`Parent builder `) } build() { Column() { Child({ aBuilder0: this.componentBuilder }) } } }this都是器其本身,不会存在传递。
6.2.2 使用场景
1、参数化传递
@Builder function GlobalBuilder1($$ : {label: string }) { Text($$.label) .width(400) .height(50) .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) } @Component struct Child { label: string = 'Child' // 无参数类,指向的componentBuilder也是无参数类型 @BuilderParam aBuilder0: () => void; // 有参数类型,指向的GlobalBuilder1也是有参数类型的方法 @BuilderParam aBuilder1: ($$ : { label : string}) => void; build() { Column() { this.aBuilder0() this.aBuilder1({label: 'global Builder label' } ) } } } @Entry @Component struct Parent { label: string = 'Parent' @Builder componentBuilder() { Text(`${this.label}`) } build() { Column() { this.componentBuilder() Child({ aBuilder0: this.componentBuilder, aBuilder1: GlobalBuilder1 }) } } }2、尾随闭包
// xxx.ets @Component struct CustomContainer { @Prop header: string; @BuilderParam closer: () => void build() { Column() { Text(this.header) .fontSize(30) this.closer() } } } @Builder function specificParam(label1: string, label2: string) { Column() { Text(label1) .fontSize(30) Text(label2) .fontSize(30) } } @Entry @Component struct CustomContainerUser { @State text: string = 'header'; build() { Column() { // 创建CustomContainer,在创建CustomContainer时,通过其后紧跟一个大括号“{}”形成尾随闭包 // 作为传递给子组件CustomContainer @BuilderParam closer: () => void的参数 CustomContainer({ header: this.text }) { Column() { specificParam('testA', 'testB') }.backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .onClick(() => { this.text = 'changeHeader'; }) } } } }6.3 @Styles装饰器
@Styles装饰器主要是定义公共样式
6.3.1 装饰指向
1、全局
// 全局 @Styles function functionName() { ... } // 在组件内 @Component struct FancyUse { @Styles fancy() { .height(100) } }2、组件内
@Component struct FancyUse { @State heightValue: number = 100 @Styles fancy() { .height(this.heightValue) .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .onClick(() => { this.heightValue = 200 }) } }6.3.2 使用场景
// 定义在全局的@Styles封装的样式 @Styles function globalFancy () { .width(150) .height(100) .backgroundColor(Color.Pink) } @Entry @Component struct FancyUse { @State heightValue: number = 100 // 定义在组件内的@Styles封装的样式 @Styles fancy() { .width(200) .height(this.heightValue) .backgroundColor(Color.Yellow) .onClick(() => { this.heightValue = 200 }) } build() { Column({ space: 10 }) { // 使用全局的@Styles封装的样式 Text('FancyA') .globalFancy () .fontSize(30) // 使用组件内的@Styles封装的样式 Text('FancyB') .fancy() .fontSize(30) } } }6.4 @Extend装饰器
@Extend用于扩展原生组件样式,作用和@Styles差不多。
6.4.1 装饰指向
@Extend仅支持定义在全局,不支持在组件内部定义
1、@Extend支持封装指定的组件的私有属性和私有事件
// @Extend(Text)可以支持Text的私有属性fontColor @Extend(Text) function fancy () { .fontColor(Color.Red) } // superFancyText可以调用预定义的fancy @Extend(Text) function superFancyText(size:number) { .fontSize(size) .fancy() }2、@Extend装饰的方法支持参数
// xxx.ets @Extend(Text) function fancy (fontSize: number) { .fontColor(Color.Red) .fontSize(fontSize) } @Entry @Component struct FancyUse { build() { Row({ space: 10 }) { Text('Fancy') .fancy(16) Text('Fancy') .fancy(24) } } }3、@Extend装饰的方法的参数可以为function
@Extend(Text) function makeMeClick(onClick: () => void) { .backgroundColor(Color.Blue) .onClick(onClick) } @Entry @Component struct FancyUse { @State label: string = 'Hello World'; onClickHandler() { this.label = 'Hello ArkUI'; } build() { Row({ space: 10 }) { Text(`${this.label}`) .makeMeClick(this.onClickHandler.bind(this)) } } }4、@Extend的参数可以为状态变量
@Extend(Text) function fancy (fontSize: number) { .fontColor(Color.Red) .fontSize(fontSize) } @Entry @Component struct FancyUse { @State fontSizeValue: number = 20 build() { Row({ space: 10 }) { Text('Fancy') .fancy(this.fontSizeValue) .onClick(() => { this.fontSizeValue = 30 }) } } }☀️6.4.2 使用场景
@Extend(Text) function fancyText(weightValue: number, color: Color) { .fontStyle(FontStyle.Italic) .fontWeight(weightValue) .backgroundColor(color) } @Entry @Component struct FancyUse { @State label: string = 'Hello World' build() { Row({ space: 10 }) { Text(`${this.label}`) .fancyText(100, Color.Blue) Text(`${this.label}`) .fancyText(200, Color.Pink) Text(`${this.label}`) .fancyText(300, Color.Orange) }.margin('20%') } }7.多态样式
stateStyles是属性方法,可以根据UI内部状态来设置样式,类似于css伪类,但语法不同。ArkUI提供以下四种状态:
- focused:获焦态
- normal:正常态
- pressed:按压态
- disabled:不可用态
7.1 基本使用
@Entry @Component struct CompWithInlineStateStyles { @State focusedColor: Color = Color.Red; normalColor: Color = Color.Green build() { Column() { Button('clickMe').height(100).width(100) .stateStyles({ normal: { .backgroundColor(this.normalColor) }, focused: { .backgroundColor(this.focusedColor) } }) .onClick(() => { this.focusedColor = Color.Pink }) .margin('30%') } } }7.2 @Styles和stateStyles联合使用
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { @Styles normalStyle() { .backgroundColor(Color.Gray) } @Styles pressedStyle() { .backgroundColor(Color.Red) } build() { Column() { Text('Text1') .fontSize(50) .fontColor(Color.White) .stateStyles({ normal: this.normalStyle, pressed: this.pressedStyle, }) } } }7.3 stateStyles里使用常规变量和状态变量
@Entry @Component struct CompWithInlineStateStyles { @State focusedColor: Color = Color.Red; normalColor: Color = Color.Green build() { Button('clickMe').height(100).width(100) .stateStyles({ normal: { .backgroundColor(this.normalColor) }, focused: { .backgroundColor(this.focusedColor) } }) .onClick(() => { this.focusedColor = Color.Pink }) .margin('30%') } }🚀写在最后
- 如果你觉得这篇内容对你还蛮有帮助,我想邀请你帮我三个小忙:
- 点赞,转发,有你们的 『点赞和评论』,才是我创造的动力。
- 关注小编,同时可以期待后续文章ing🚀,不定期分享原创知识。
- 想要获取文中提到的学习资料,请点击→全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
- 或者关注小编后私信回复【666】也可获取资料哦~~

-
猜你喜欢
网友评论
- 搜索
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
