谨以此文巩固算法知识
本来只有六道题的,后来改成26道了,学业繁忙,暂时不写解析了,有时间会补充
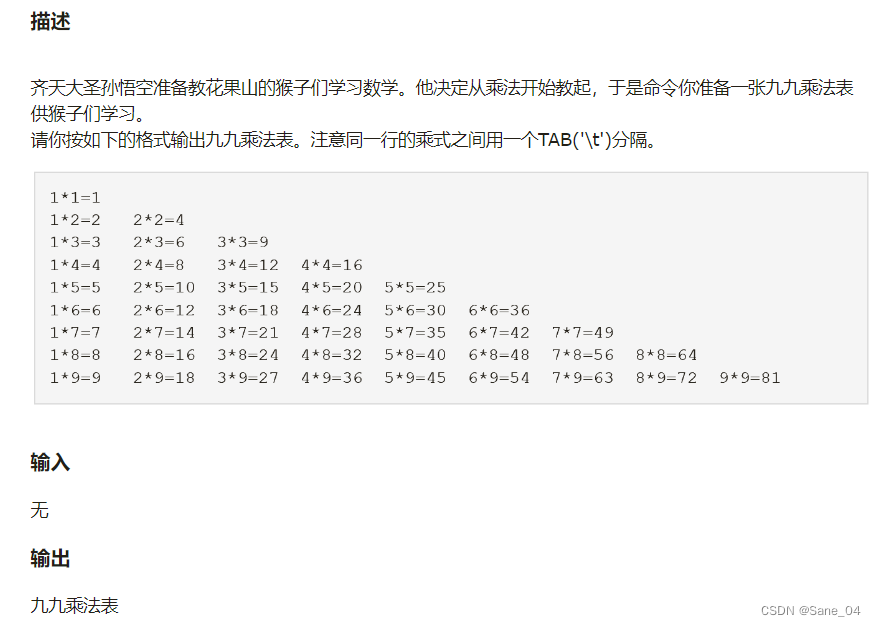
题目一:九九乘法表
题目链接:OpenJudge - 001:九九乘法表
思路分析:
分析题目描述可知,共输出9行,每行的列由1至9递增,因此考虑双层嵌套循环
外层循环控制行数,内层循环控制列数
下面分析循环的控制条件
第一行有一列,第二行有二列,即行和列的关系为第n行有n列,即当外层循环到n的时候,内层循环要输出n次
所以只需外层循环从1循环到9,内层循环从1循环到当前外层循环的值即可,下面是代码实现
代码实现:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){
for (int j=1;j<=i;j++){
System.out.printf(j+"*"+i+"="+j*i+"\t");
}
System.out.println(); //这里是因为行与行间有换行符
}
}
}
题目二:斐波那契数列
题目链接:OpenJudge - 002:斐波那契数列

思路分析:
首先需要明确斐波那契数列的定义
如1,3,4,7,11
这种第1,2项为随机值,自第3项开始每项值为前两项之和的数列称为斐波那契数列
公式表示即为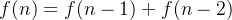
题目给定的输入x,y,n分别为数列的第1,2项以及数列长度
要求的输出为以x第一项,y为第二项,总长度为n的数列
那么我们需要知道该数列的每一项的值
我们现在已知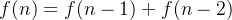
即我们可以根据此公式求出该数列任一项的值
求法:
定义一个方法int fib(int x,int y,int n),该方法返回以x为第一项,y为第二项的数列的第n项的值
例如输入的n为5
那么有
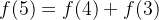

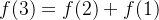
而f(2)和f(1)的值是已知的,因此可以用递推的方法求出f(5),同理求出f(n),我们代码采用递归形式实现
int fib(int x,int y,int n){
if(n==1)
return x;
if(n==2)
return y;
return fib(x,y,n-1)+fib(x,y,n-2);
}
现在我们可以求出该数列的任意一项,因此只需要从1循环至n,循环内调用fib方法即可输出该数列
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(new Main().fib(x,y,i) + " ");
}
}
public int fib(int x,int y,int n) {
if (n == 1)
return x;
if (n == 2)
return y;
return fib(x,y,n - 1) + fib(x,y,n - 2);
}
}
题目三:约瑟夫环问题
题目链接:OpenJudge - 003:约瑟夫问题
思路分析:
下面是我的错误想法,相信也是很多人的想法,不过误打误撞推导出了正确公式,仅供避雷参考
我们假设有7只猴子,数到3的猴子出圈,即n=7,m=3
如上图所示,画圈的编号表示出圈的猴子编号
第一次选出圈猴时,从1开始数,数到3,第二次选出圈猴时,应从4开始数,因此第二次选出圈猴时开头的编号为4,以此类推,最后剩下4为大王
根据上图,我们可以知道,第一次选出圈猴时,开头的编号必然为1,而大王的编号必然是上图中最后一行的开头的编号,因此我们只要找到行与行间编号的映射关系即可知道大王的编号
观察上图画圈的编号,3->6->2->7->5,对应关系为
[f(1)+m]%n=f(2)
[f(2)+m]%n=f(3)
即[f(n)+m]%n=f(n+1) 其中f(n)表示第n行对应的编号
可化为[f(n-1)+m]%n=f(n)
即f(n) = [f(n-1)+m]%n
这个公式是怎么得到的?
我们看第一行,编号3在第一个的第三个位置,下一行的第一个位置必然是(3+1)%7,那么下一行的第三个位置就是(3+1+2)%7,即(3+m)%n
此公式对任一列都适用,我们代入第一列试一试
f(1) = 1
f(2) = [f(1)+3]%7 = 4
f(3) = [f(2)+3]%7 = 0
可以看到,到f(3)这里出现了问题,由于取余符号的特性,7%7,等于0而不是7,这里出现了错误,因此需要修改一下公式,f(n) = [f(n-1)+m-1]%n+1,这样就避免了出现7%7这种情况
至此 我认为该问题已经解决,然而实际上每次出圈总人数都会发生变化,此公式并不适用于求每次出圈的编号即只对f(n)和f(1)适用
下面是明烛大佬给出的数学推导过程 这或许是你能找到的最详细约瑟夫环数学推导! - 知乎
对于不是单纯搞算法的我们来说,这些数学类知识只需要稍微理解记住即可,不必深究
公式为:f(n) = [f(n-1)+m-1]%n+1
已知f(1)=1,那么f(n)只需要递归即可
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = 1, m = 1;
while (n != 0 && m != 0) {
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
if(n==0&&m==0)
break;
System.out.println(new Main().yuesefu(n, m));
}
}
public int yuesefu(int n, int k) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return (yuesefu(n - 1, k) + k - 1) % n + 1;
}
}
}
题目四:全排列
原题链接:OpenJudge - 004:全排列

思路分析:
首先需要知道字母序的定义,用大白话来说,就是先比较第一个字符, 小的排前面,如果第一个字符相同,则比较第二个字符,小的排前面,以此类推
题目要求字符串内所有字符的所有排列,我们首先想到的肯定是暴力循环,但是显然我们并不知道循环的层数,因此采用递归回溯的形式求解(递归实质也是暴力循环,但是可以通过结束条件控制循环层数)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
static ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
char result[] = new char[7];
int result_index = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
char a[] = str.toCharArray();
new Main().backtrack(a, 0, new boolean[a.length]);
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(array.get(i));
}
}
public void backtrack(char a[], int k, boolean used[]) {
if (k >= a.length) {
if (result_index == a.length) {
String str = new String(result, 0, result_index);
array.add(str);
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
result[result_index++] = a[i];
used[i] = true;
backtrack(a, k + 1, used);
result_index--;
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
array是String类型的集合,用于存储所有的排列好的字符串(这里也可以用String数组,但是会造成不必要的空间浪费)
result用于接收每次递归的字符,当达到原字符串的长度时,转成String存储到array中
递归回溯实际上就是对树的遍历
我们假设有a,b,c三个字符,则其树的结构为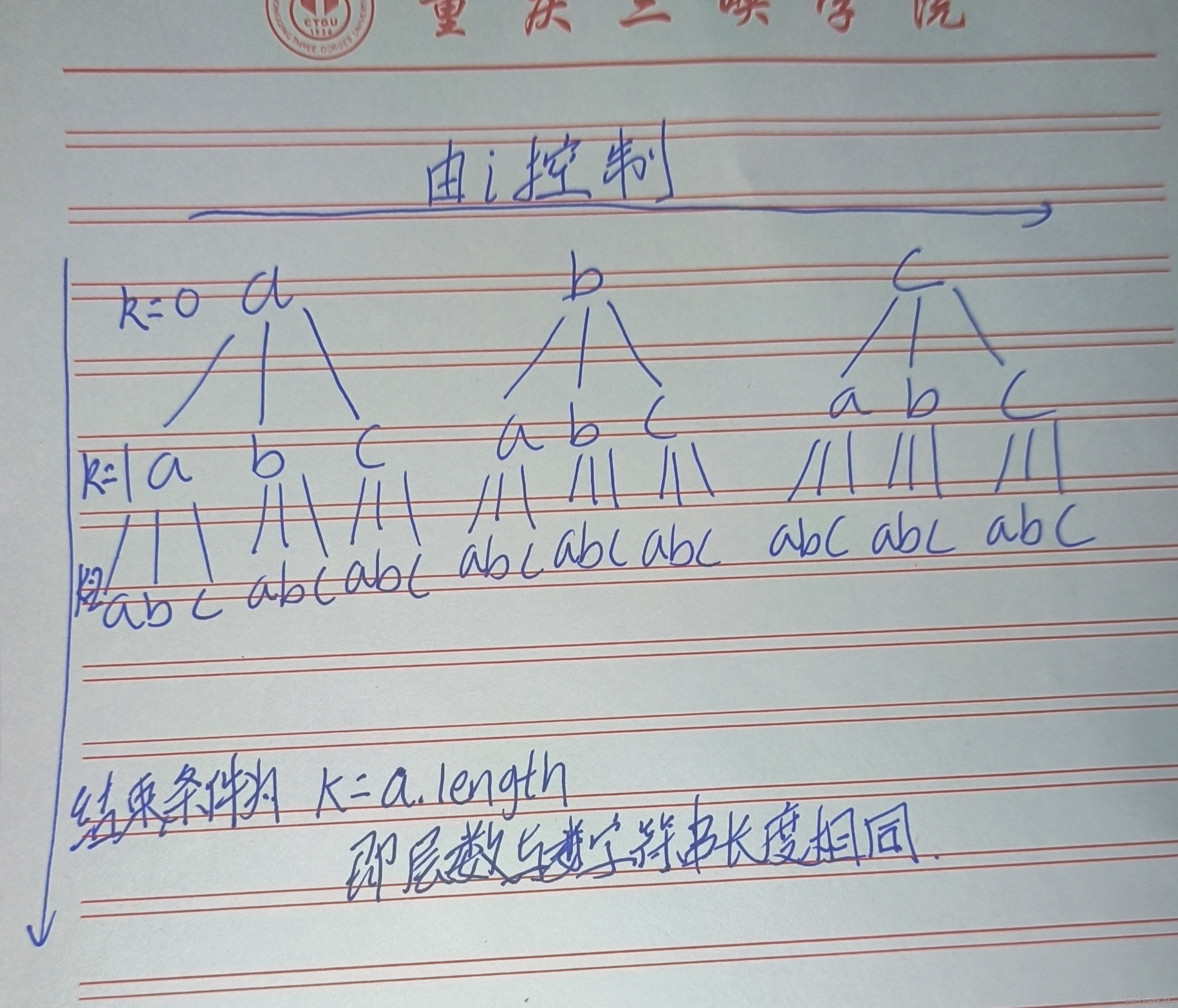
由上图可知在result中同一元素会重复,因此使用used数组的boolean值来控制是否添加该元素,元素进入result数组之后,其对应的used数组的值改为true,这样在这一条路径上该元素不会再次进入result数组,在回溯时将该元素的used值设置为false,这样可以在同一层级上的其他路径上再次进入result数组,至于具体代码实现过程,实在繁琐,不再叙述
代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
static ArrayList array = new ArrayList();
char result[] = new char[7];
int result_index = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.next();
char a[] = str.toCharArray();
new Main().backtrack(a, 0, new boolean[a.length]);
for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(array.get(i));
}
}
public void backtrack(char a[], int k, boolean used[]) {
if (k >= a.length) {
if (result_index == a.length) {
String str = new String(result, 0, result_index);
array.add(str);
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
result[result_index++] = a[i];
used[i] = true;
backtrack(a, k + 1, used);
result_index--;
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
题目五:统计质数个数
原题链接:OpenJudge - 005:统计质数个数

思路分析:
首先需要知道质数(素数)的定义,大白话来讲,如果一个数除了可以整除自身外,没有其他可以整除的数,那么这个数就是质数,如2,3,5,7
那么我们要知道一个数是不是素数,只需要知道其除了自身,是否还可以整除其他数
如判断7是不是质数,我们可以从2开始遍历到6,如果之间存在7%i==0,即存在i可以被7整除,那么7就不是质数,如果不存在,则7是质数,显然(7%i!)=0 (i=2,3,4,5,6),因此7是质数
判断8是不是质数,我们从2遍历到7,显然8%2==0,因此8不是质数
但是此方法时间复杂度较高,可以做适当优化,我们知道,一个数的因数一定是关于其二次根对称的,以16为例,sqrt(16)=4,16=2*8,16=4*4,16=8*2,我们可以观察到,2,8是关于4对称的,那么如果在4之前没有数可以被16整除,则在4-15也不会有数可以被16整除,因此我们只需要遍历到sqrt(n)即可
知道了怎么判断一个数为质数,那么此问题只需要再嵌套一层循环从n遍历到m
即可
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int count = 0;
while (n <= m) {
if (n >= 2) {
int s = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n / i; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
s++;
break;
}
}
if (s == 0)
count++;
}
n++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
题目六:水仙花数
原题链接:OpenJudge - 006:水仙花数(daffodil)

思路分析:
首先明确什么是水仙花数,对于一个三位数abc,如果a^3+b^3+c^3=abc,那么该数就是水仙花数,如153
此题的考点在于对于一个三位数如何单独取出其个位数,十位数,百位数
如153,其个位数为153%10=3,
其十位数为(153/10)%10=5,
其百位数为(153/10/10)%10=1
知道这一点 这道题就基本完成了
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 100; i <= n; i++) {
if ((i % 10) * (i % 10) * (i % 10) + (i / 10 % 10) * (i / 10 % 10) * (i / 10 % 10) + (i / 100 % 10) * (i / 100 % 10) * (i / 100 % 10) == i)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
题目七:八皇后问题
代码实现:
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
static int num = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[] = new int[8];
new Main().backTrack(a, 0);
}
void backTrack(int a[], int k) {
if (k == 8) {
System.out.println("No. " + num++);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if (j == search(a, i))
System.out.print("1 ");
else
System.out.print("0 ");
}
System.out.println();
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if (check(a, i, k)) {
a[k] = i;
backTrack(a, k + 1);
a[k] = 0;
}
}
}
boolean check(int a[], int i, int k) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
if (a[j] == i || Math.abs(a[j] - i) == Math.abs(j - k)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int search(int a[], int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if (a[j] == i)
return j;
}
return 0;
}
}
题目八:数字三角形
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[][] a = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
a[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int[][] dp = new int[N][N];
dp[0][0] = a[0][0];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0] + a[i][0];
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]) + a[i][j];
}
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, dp[N-1][i]);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}
题目九:放苹果
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while (t-- > 0) {
int M = sc.nextInt();
int N = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(countWays(M, N));
}
}
public static long countWays(int M, int N) {
if (M <= 1 || N == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (M < N) {
return countWays(M, M);
}
return countWays(M, N - 1) + countWays(M - N, N);
}
}
题目十:鸣人和佐助
代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int hang, lie, chark;
static Queue que = new ArrayDeque<>();
static char map[][];
static xy mingren;
static boolean visited[][][];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
hang = sc.nextInt();
lie = sc.nextInt();
chark = sc.nextInt();
map = new char[hang + 2][lie + 2];
visited = new boolean[hang + 1][lie + 1][chark + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= hang; i++) {
String str = sc.next();
for (int j = 1; j <= lie; j++) {
map[i][j] = str.charAt(j - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= hang; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= lie; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == '@') {
mingren = new xy(i, j, chark);
break;
}
}
}
visited[mingren.x][mingren.y][chark] = true;
bfs();
}
static void bfs() {
int dx[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
que.add(mingren);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
xy a = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int new_x = a.x + dx[i];
int new_y = a.y + dy[i];
if (new_x > 0 && new_x <= hang && new_y > 0 && new_y <= lie && !visited[new_x][new_y][a.charkla]) {
switch (map[new_x][new_y]) {
case '*':
xy temp = new xy(new_x, new_y, a.charkla);
temp.dist = a.dist + 1;
visited[new_x][new_y][a.charkla] = true;
que.add(temp);
break;
case '+':
System.out.println(a.dist + 1);
return;
case '#':
if (a.charkla != 0) {
xy temp2 = new xy(new_x, new_y, a.charkla - 1);
temp2.dist = a.dist + 1;
visited[new_x][new_y][a.charkla] = true;
que.add(temp2);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("-1");
}
}
class xy {
int x, y, charkla;
int dist;
public xy(int x, int y, int charkla) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.charkla = charkla;
}
}
题目十一:电影节
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int n;
static ArrayList arrays;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
arrays = new ArrayList<>();
while ((n = sc.nextInt()) != 0) {
while (n-- > 0) {
arrays.add(new movie(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt()));
}
Collections.sort(arrays, new Comparator() {
public int compare(movie m1, movie m2) {
return m1.end - m2.end;
}
});
int last_end = 0;
int count = 0;
for (movie m : arrays) {
int start = m.start;
int end = m.end;
if (start>=last_end) {
count++;
last_end = end;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
arrays.clear();
}
}
}
class movie {
int start;
int end;
public movie(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
题目十二:数制转换
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
String str = sc.next();
int b = sc.nextInt();
if (str.equals("0")) {
System.out.println("0");
return;
}
long ten_n = to_ten(str, a);
String s_turn = to_b(ten_n, b);
System.out.print(s_turn);
}
public static long to_ten(String str, int a) {
char num[] = str.toCharArray();
long ten_n = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = num.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (num[i] >= 'A' && num[i] <= 'F')
ten_n += (num[i] - 'A' + 10) * Math.pow(a, count++);
else if (num[i] >= 'a' && num[i] <= 'f')
ten_n += (num[i] - 'a' + 10) * Math.pow(a, count++);
else
ten_n += (num[i] - '0') * Math.pow(a, count++);
}
return ten_n;
}
public static String to_b(long ten_n, int b) {
String s_turn = "";
for (int i = 0; ten_n > 0; i++) {
long temp = ten_n % b;
if (temp >= 0 && temp <= 9) {
s_turn = (temp + "") + s_turn;
} else {
s_turn = (char) ('A' + (temp - 10)) + s_turn;
}
ten_n /= b;
}
return s_turn;
}
}
题目十三:胡
代码实现
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int A[] = new int[10];
static ArrayList que = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str;
while (true) {
str = sc.nextLine().replaceAll(" ", "");
if (str.charAt(0) == '0')
break;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
A[(int) (str.charAt(i) - '0')]++;
}
if ((str.length() - 2) % 3 != 0) {
System.out.println("XIANGGONG");
Arrays.fill(A, 0);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (A[i] >= 2)
que.add(i);
}
if (que.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("BUHU");
Arrays.fill(A, 0);
} else {
boolean s = true;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
s = true;
int temp = que.remove(0);
int B[] = Arrays.copyOf(A, 10);
B[temp] -= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
B[i] %= 3;
}
boolean turn = true;
while (turn) {
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
turn = false;
if (B[j] > 0) {
turn = true;
count++;
if (count % 3 == 0) {
B[j - 2]--;
B[j - 1]--;
B[j]--;
count = 0;
} else turn = false;
} else count = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (B[i] != 0) {
s = false;
}
}
if (s) {
System.out.println("HU");
Arrays.fill(A, 0);
que.clear();
break;
}
}
if (!s) {
System.out.println("BUHU");
}
}
}
Arrays.fill(A, 0);
que.clear();
}
}
}
题目十四:垂直直方图
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static char map[][];
static int counts[] = new int[26];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) {
if (str.charAt(j) >= 'A' && str.charAt(j) <= 'Z')
counts[str.charAt(j) - 'A']++;
}
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, counts[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= max; i++) {
if (i == max)
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
System.out.print((char) ('A' + j));
System.out.print(' ');
}
else
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if (i >= max - counts[j])
System.out.print("*");
else
System.out.print(' ');
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
题目十五:算24
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static double a[] = new double[4];
static boolean suc = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean ctn = true;
while (true) {
suc = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextDouble();
}
if (a[0] == 0 && a[1] == 0 && a[2] == 0 && a[3] == 0) {
break;
}
dfs(0, a, 0);
System.out.println(suc ? "YES" : "NO");
}
}
static void dfs(int k, double b[], double lastsum) {
if (b.length == 1) {
if (Math.abs(b[0] - 24) < 1e-6)
suc = true;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++) {
if (i != j) {
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++) {
switch (l) {
case 0:
double temp[] = new double[b.length - 1];
for (int m = 0, p = 0; p < b.length; p++) {
if (p != i && p != j)
temp[m++] = b[p];
}
temp[temp.length - 1] = b[i] + b[j];
dfs(k + 1, temp, b[i] + b[j]);
break;
case 1:
double temp1[] = new double[b.length - 1];
for (int m = 0, p = 0; p < b.length; p++) {
if (p != i && p != j)
temp1[m++] = b[p];
}
temp1[temp1.length - 1] = b[i] - b[j];
dfs(k + 1, temp1, b[i] - b[j]);
break;
case 2:
double temp2[] = new double[b.length - 1];
for (int m = 0, p = 0; p < b.length; p++) {
if (p != i && p != j)
temp2[m++] = b[p];
}
temp2[temp2.length - 1] = b[i] * b[j];
dfs(k + 1, temp2, b[i] * b[j]);
break;
case 3:
if (b[j] != 0) {
double temp3[] = new double[b.length - 1];
for (int m = 0, p = 0; p < b.length; p++) {
if (p != i && p != j)
temp3[m++] = b[p];
}
temp3[temp3.length - 1] = b[i] / b[j];
dfs(k + 1, temp3, b[i] / b[j]);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
题目十六:Knight Moves
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int n;
static boolean map[][];
static boolean visited[][];
static ArrayList que = new ArrayList<>();
static int l;
static int dist[][];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
while (n-- > 0) {
l = sc.nextInt();
map = new boolean[l][l];
visited = new boolean[l][l];
dist = new int[l][l];
int startx = sc.nextInt();
int starty = sc.nextInt();
visited[startx][starty] = true;
int endx = sc.nextInt();
int endy = sc.nextInt();
if (startx == endx && starty == endy) {
System.out.println(0);
continue;
}
map[endx][endy] = true;
bfs(startx, starty);
System.out.println(dist[endx][endy]);
que.clear();
}
}
static void bfs(int startx, int starty) {
que.add(new xy(startx, starty));
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
xy temp = que.remove(0);
int x = temp.x;
int y = temp.y;
if (x - 2 >= 0) {
if (y - 1 >= 0 && !visited[x - 2][y - 1]) {
visited[x - 2][y - 1] = true;
dist[x - 2][y - 1] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x - 2][y - 1]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x - 2, y - 1));
}
if (y + 1 < l && !visited[x - 2][y + 1]) {
visited[x - 2][y + 1] = true;
dist[x - 2][y + 1] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x - 2][y + 1]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x - 2, y + 1));
}
}
if (x - 1 >= 0) {
if (y - 2 >= 0 && !visited[x - 1][y - 2]) {
visited[x - 1][y - 2] = true;
dist[x - 1][y - 2] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x - 1][y - 2]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x - 1, y - 2));
}
if (y + 2 < l && !visited[x - 1][y + 2]) {
visited[x - 1][y + 2] = true;
dist[x - 1][y + 2] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x - 1][y + 2]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x - 1, y + 2));
}
}
if (x + 1 < l) {
if (y - 2 >= 0 && !visited[x + 1][y - 2]) {
visited[x + 1][y - 2] = true;
dist[x + 1][y - 2] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x + 1][y - 2]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x + 1, y - 2));
}
if (y + 2 < l && !visited[x + 1][y + 2]) {
visited[x + 1][y + 2] = true;
dist[x + 1][y + 2] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x + 1][y + 2]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x + 1, y + 2));
}
}
if (x + 2 < l) {
if (y - 1 >= 0 && !visited[x + 2][y - 1]) {
visited[x + 2][y - 1] = true;
dist[x + 2][y - 1] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x + 2][y - 1]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x + 2, y - 1));
}
if (y + 1 < l && !visited[x + 2][y + 1]) {
visited[x + 2][y + 1] = true;
dist[x + 2][y + 1] = dist[x][y] + 1;
if (map[x + 2][y + 1]) {
return;
}
que.add(new xy(x + 2, y + 1));
}
}
}
}
}
class xy {
int x, y;
public xy(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
题目十七:末位零
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int N;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
while (N-- > 0) {
int count = 0;
int m = sc.nextInt();
while (m > 0) {
count += m / 5;
m /= 5;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
题目十八:二叉树
代码实现
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int m, n;
static int sum = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
m = sc.nextInt();
n = sc.nextInt();
if (m == 0 && n == 0)
break;
sum = 0;
num(m, n, 0);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
static void num(int m, int n, int hang) {
if (2 * m <= n) {
hang++;
num(2 * m, n, hang);
} else {
if (hang == 0) {
sum = 1;
} else {
int a = 1;
sum = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < hang; i++) {
a *= 2;
sum += a;
}
if (m + 2 * a - 1 >= n)
sum = sum + (n - m) + 1;
else
sum = sum + (m + 2 * a - 1 - m) + 1;
}
}
}
}
题目十九:大整数加法
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str1 = sc.next();
String str2 = sc.next();
ArrayList al1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList al2 = new ArrayList<>();
boolean i1 = true;
boolean i2 = true;
boolean zero1 = true;
boolean zero2 = true;
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
if (str1.charAt(i) != '0')
zero1 = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length(); i++) {
if (str2.charAt(i) != '0')
zero2 = false;
}
if (zero1 && zero2) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
if (i1) {
if ((str1.charAt(i) - '0') == 0)
continue;
else
i1 = false;
}
al1.add(str1.charAt(i) - '0');
}
for (int i = 0; i < str2.length(); i++) {
if (i2) {
if ((str2.charAt(i) - '0') == 0)
continue;
else
i2 = false;
}
al2.add(str2.charAt(i) - '0');
}
Collections.reverse(al1);
Collections.reverse(al2);
ArrayList al3 = new ArrayList<>();
boolean jinwei = false;
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(al2.size(), al1.size()); i++) {
int temp = 0;
if (jinwei) {
temp = al1.get(i) + al2.get(i) + 1;
jinwei = false;
} else
temp = al1.get(i) + al2.get(i);
al3.add(temp % 10);
if (temp >= 10) {
jinwei = true;
}
}
if (al1.size() > al2.size()) {
for (int i = al2.size(); i < al1.size(); i++) {
int temp = 0;
if (jinwei) {
temp = al1.get(i) + 1;
jinwei = false;
} else
temp = al1.get(i);
al3.add(temp % 10);
if (temp >= 10) {
jinwei = true;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = al1.size(); i < al2.size(); i++) {
int temp = 0;
if (jinwei) {
temp = al2.get(i) + 1;
jinwei = false;
} else
temp = al2.get(i);
al3.add(temp % 10);
if (temp >= 10) {
jinwei = true;
}
}
}
if (jinwei)
al3.add(1);
Collections.reverse(al3);
for (int i = 0; i < al3.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(al3.get(i));
}
}
}
题目二十:显示器
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static boolean shang[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean zhong[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean xia[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean start_shang[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean start_xia[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean end_shang[] = new boolean[10];
static boolean end_xia[] = new boolean[10];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
int size = sc.nextInt();
int show_num = sc.nextInt();
if (show_num == 0 && size == 0)
break;
shang[1] = true;
shang[4] = true;
zhong[0] = true;
zhong[1] = true;
zhong[7] = true;
xia[1] = true;
xia[4] = true;
xia[7] = true;
start_shang[0] = true;
start_shang[4] = true;
start_shang[5] = true;
start_shang[6] = true;
start_shang[8] = true;
start_shang[9] = true;
start_xia[0] = true;
start_xia[2] = true;
start_xia[6] = true;
start_xia[8] = true;
end_shang[0] = true;
end_shang[1] = true;
end_shang[2] = true;
end_shang[3] = true;
end_shang[4] = true;
end_shang[7] = true;
end_shang[8] = true;
end_shang[9] = true;
end_xia[0] = true;
end_xia[1] = true;
end_xia[3] = true;
end_xia[4] = true;
end_xia[5] = true;
end_xia[6] = true;
end_xia[7] = true;
end_xia[8] = true;
end_xia[9] = true;
String num_str = String.valueOf(show_num);
int len = num_str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * size + 3; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < len; k++) {
int temp = num_str.charAt(k) - '0';
if (i == 0 || i == size + 1 || i == 2 * size + 2)
System.out.print(" ");
else {
if (i < size + 1) {
if (start_shang[temp])
System.out.print("|");
else System.out.print(" ");
}
if (i > size + 1) {
if (start_xia[temp])
System.out.print("|");
else System.out.print(" ");
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
if (i == 0) {
if (shang[temp]) {
System.out.print(" ");
} else System.out.print("-");
} else if (i == size + 1) {
if (zhong[temp]) {
System.out.print(" ");
} else System.out.print("-");
} else if (i == 2 * size + 2) {
if (xia[temp]) {
System.out.print(" ");
} else System.out.print("-");
} else {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
if (i == 0 || i == size + 1 || i == 2 * size + 2)
System.out.print(" ");
else {
if (i < size + 1) {
if (end_shang[temp])
System.out.print("|");
else System.out.print(" ");
}
if (i > size + 1) {
if (end_xia[temp])
System.out.print("|");
else System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
题目二十一:棋盘问题
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int n, k;
static char map[][];
static int count = 0;
static boolean now_map[][];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
n = sc.nextInt();
k = sc.nextInt();
if (n == -1 && k == -1) {
break;
}
map = new char[n + 1][n + 1];
now_map = new boolean[n + 1][n + 1];
if (k <= 0 || n <= 0) {
System.out.println(0);
continue;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
String str = sc.next();
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
map[i][j] = str.charAt(j - 1);
}
}
dfs(1, 0);
System.out.println(count);
count = 0;
}
}
static void dfs(int ceng, int pulled) {
if (pulled >= k) {
count++;
return;
}
if (ceng > n)
return;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (map[ceng][i] == '#' && check(ceng, i)) {
now_map[ceng][i] = true;
dfs(ceng + 1, pulled + 1);
now_map[ceng][i] = false;
}
}
dfs(ceng + 1, pulled);
}
static boolean check(int i, int j) {
for (int l = 1; l < i; l++) {
if (now_map[l][j])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
题目二十二:金币
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int day;
static int sum = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
day = sc.nextInt();
if (day == 0)
break;
answer(day);
System.out.println(day + " " + sum);
sum = 0;
}
}
static void answer(int day) {
int jiange = 1;
int last_jiange = jiange;
int gold = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= day; i++) {
sum += gold;
jiange--;
if (jiange == 0) {
jiange = last_jiange + 1;
last_jiange = jiange;
gold++;
}
}
}
}
题目二十三:英语数字转换器
代码实现:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map dict = new HashMap<>();
dict.put("negative", -1);
dict.put("zero", 0);
dict.put("one", 1);
dict.put("two", 2);
dict.put("three", 3);
dict.put("four", 4);
dict.put("five", 5);
dict.put("six", 6);
dict.put("seven", 7);
dict.put("eight", 8);
dict.put("nine", 9);
dict.put("ten", 10);
dict.put("eleven", 11);
dict.put("twelve", 12);
dict.put("thirteen", 13);
dict.put("fourteen", 14);
dict.put("fifteen", 15);
dict.put("sixteen", 16);
dict.put("seventeen", 17);
dict.put("eighteen", 18);
dict.put("nineteen", 19);
dict.put("twenty", 20);
dict.put("thirty", 30);
dict.put("forty", 40);
dict.put("fifty", 50);
dict.put("sixty", 60);
dict.put("seventy", 70);
dict.put("eighty", 80);
dict.put("ninety", 90);
dict.put("hundred", 100);
dict.put("thousand", 1000);
dict.put("million", 1000000);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if (line.length() == 0) {
break;
}
long ans = 0;
long t = 0;
String[] words = line.split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
if (dict.containsKey(word)) {
int value = dict.get(word);
if (value == -1) {
System.out.print("-");
} else if (value == 100) {
t *= value;
} else if (value == 1000 || value == 1000000) {
t *= value;
ans += t;
t = 0;
} else {
t += value;
}
}
}
ans += t;
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
}
题目二十四:重建二叉树
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int index = 0;
static String str1, str2;
static ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
if (!sc.hasNext())
break;
str1 = sc.next();
if (!sc.hasNext())
break;
str2 = sc.next();
digui(str2, 0, null);
bianli(nodes.get(0));
System.out.println();
nodes.clear();
index = 0;
}
}
static void digui(String str2, int dir, Node last_node) {
if (str2.isEmpty())
return;
if (index == str1.length())
return;
char ch = str1.charAt(index);
Node node = new Node(ch);
nodes.add(node);
index++;
if (last_node != null) {
if (dir == 0) {
last_node.left = node;
} else last_node.right = node;
}
String new_array[] = str2.split(String.valueOf(ch));
if (new_array.length > 0) {
digui(new_array[0], 0, node);
}
if (new_array.length > 1)
digui(new_array[1], 1, node);
}
static void bianli(Node node) {
if (node.left != null)
bianli(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
bianli(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data);
}
}
class Node {
char data;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
题目二十五:汉诺塔问题(Tower of Hanoi)
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int n;
static int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3;
static char ch[];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
ch = new char[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ch[i] = sc.next().charAt(0);
}
tower(a, b, c, n, n);
}
static void tower(int t1, int t2, int t3, int num, int bianhao) {
if (num == 1) {
char ch1 = 0, ch2 = 0;
switch (t1) {
case 1:
ch1 = ch[0];
break;
case 2:
ch1 = ch[1];
break;
case 3:
ch1 = ch[2];
break;
}
switch (t3) {
case 1:
ch2 = ch[0];
break;
case 2:
ch2 = ch[1];
break;
case 3:
ch2 = ch[2];
break;
}
System.out.println(bianhao + ":" + ch1 + "->" + ch2);
return;
}
tower(t1, t3, t2, num - 1, bianhao - 1);
tower(t1, t2, t3, 1, bianhao);
tower(t2, t1, t3, num - 1, bianhao - 1);
}
}
题目二十六:数字方格
代码实现:
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author Sane
* @version 1.0
*/
class Main {
static int a1, a2, a3;
static int n;
static int max;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
if ((i + j) % 2 == 0 && (j + k) % 3 == 0 && (i + j + k) % 5 == 0)
max = Math.max(max, i + j + k);
}
}
}
System.out.println(max);
}
} 猜你喜欢
- 3月前梦见大蟒蛇的周公解梦解析
- 3月前梦见吃面条的寓意解析
- 3月前梦中见斗殴流血的心理解析
- 3月前梦见打死蛇头预示什么征兆
- 3月前梦中遇袭的心理分析与应对
- 3月前梦见顺产顺利预示美好征兆
- 3月前梦中初尝飞翔的生涩体验
- 3月前周公梦册查码解梦指南
- 3月前梦中被狗追逐的深层心理解析
- 3月前梦见杀猪的周公解梦解析
网友评论
- 搜索
- 最新文章
- 热门文章

