regularization_linear_regression.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class RegularizationLinearRegression:
"""
线性回归 + 正则化,梯度下降法 + 闭式解求解模型系数
1、数据的预处理:是否训练偏置项fit_intercept(默认True),是否标准化normalized(默认True)
2、模型的训练:fit(self, x_train, y_train):闭式解form,梯度下降法:grad
3、模型的预测,predict(self, x_test)
4、均方误差,判决系数
5、模型预测可视化
"""
def __init__(self, solver="grad", fit_intercept=True, normalize=True, alpha=0.05,
max_epochs=300, batch_size=20, l1_ratio=None, l2_ratio=None, en_rou=None):
"""
:param solver: 求解方法:form是闭式解,grad是梯度
:param fit_intercept: 是否训练偏置项
:param normalize: 是否标准化
:param alpha: 学习率
:param max_epochs: 最大迭代次数
:param batch_size: 批量大小,若为1,则为随机梯度,若为训练集样本量,则为批量梯度,否则为小批量梯度
:param l1_ratio: LASSO回归惩罚项系数
:param l2_ratio: 岭回归惩罚项系数
:param en_rou: 弹性网络权衡L1和L2的系数
"""
self.solver = solver # 求解方法
self.fit_intercept = fit_intercept # 线性模型的常数项。也即偏置bias,模型中的theta0
self.normalize = normalize # 是否标准化数据
self.alpha = alpha # 学习率
if l1_ratio:
if l1_ratio < 0:
raise ValueError("惩罚项系数不能为负数")
self.l1_ratio = l1_ratio # LASSO回归惩罚项系数
if l2_ratio:
if l2_ratio < 0:
raise ValueError("惩罚项系数不能为负数")
self.l2_ratio = l2_ratio # 岭回归惩罚项系数
if en_rou:
if en_rou > 1 or en_rou < 0:
raise ValueError("弹性网络权衡系数范围在[0, 1]")
self.en_rou = en_rou # 弹性网络权衡L1和L2的系数
self.max_epochs = max_epochs
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.theta = None # 训练权重系数
if normalize:
self.feature_mean, self.feature_std = None, None # 特征的均值,标准方差
self.mse = np.infty # 训练样本的均方误差
self.r2, self.r2_adj = 0.0, 0.0 # 判定系数和修正判定系数
self.n_samples, self.n_features = 0, 0 # 样本量和特征数
self.train_loss, self.test_loss = [], [] # 存储训练过程中的训练损失和测试损失
def init_params(self, n_features):
"""
初始化参数
如果训练偏置项,也包含了bias的初始化
:return:
"""
self.theta = np.random.randn(n_features, 1) * 0.1
def fit(self, x_train, y_train, x_test=None, y_test=None):
"""
样本的预处理,模型系数的求解,闭式解公式 + 梯度方法
:param x_train: 训练样本集 m*k
:param y_train: 训练目标集 m*1
:param x_test: 测试样本集 n*k
:param y_test: 测试目标集 n*1
:return:
"""
if self.normalize:
self.feature_mean = np.mean(x_train, axis=0) # 样本均值
self.feature_std = np.std(x_train, axis=0) + 1e-8 # 样本方差
x_train = (x_train - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std # 标准化
if x_test is not None:
x_test = (x_test - self.feature_mean) / self.feature_std # 标准化
if self.fit_intercept:
x_train = np.c_[x_train, np.ones_like(y_train)] # 添加一列1,即偏置项样本
if x_test is not None and y_test is not None:
x_test = np.c_[x_test, np.ones_like(y_test)] # 添加一列1,即偏置项样本
self.init_params(x_train.shape[1]) # 初始化参数
# 训练模型
if self.solver == "grad":
self._fit_gradient_desc(x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test) # 梯度下降法训练模型
elif self.solver == "form":
self._fit_closed_form_solution(x_train, y_train)
else:
raise ValueError("仅限于闭式解form或梯度下降算法grad")
def _fit_closed_form_solution(self, x_train, y_train):
"""
线性回归的闭式解,单独函数,以便后期扩充维护
:param x_train: 训练样本集
:param y_train: 训练目标集
:return:
"""
# pinv伪逆,即(A^T * A)^(-1) * A^T
if self.l2_ratio is None:
self.theta = np.linalg.pinv(x_train).dot(y_train) # 非正则化
# xtx = np.dot(x_train.T, x_train) + 0.01 * np.eye(x_train.shape[1]) # 按公式书写
# self.theta = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(xtx), x_train.T).dot(y_train)
elif self.l2_ratio:
self.theta = np.linalg.inv(x_train.T.dot(x_train) + self.l2_ratio *
np.eye(x_train.shape[1])).dot(x_train.T).dot(y_train)
else:
pass
def _fit_gradient_desc(self, x_train, y_train, x_test=None, y_test=None):
"""
三种梯度下降求解 + 正则化:
(1)如果batch_size为1,则为随机梯度下降法
(2)如果batch_size为样本量,则为批量梯度下降法
(3)如果batch_size小于样本量,则为小批量梯度下降法
:return:
"""
train_sample = np.c_[x_train, y_train] # 组合训练集和目标集,以便随机打乱样本
# np.c_水平方向连接数组,np.r_竖直方向连接数组
# 按batch_size更新theta,三种梯度下降法取决于batch_size的大小
best_theta, best_mse = None, np.infty # 最佳训练权重与验证均方误差
for i in range(self.max_epochs):
self.alpha *= 0.95
np.random.shuffle(train_sample) # 打乱样本顺序,模拟随机化
batch_nums = train_sample.shape[0] // self.batch_size # 批次
for idx in range(batch_nums):
# 取小批量样本,可以是随机梯度(1),批量梯度(n)或者是小批量梯度(
test_reg_linear_regression.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from polynomial_feature import PolynomialFeatureData
from regularization_linear_regression import RegularizationLinearRegression
def objective_fun(x):
"""
目标函数
:param x:
:return:
"""
return 0.5 * x ** 2 + x + 2
np.random.seed(42)
n = 30 # 采样数据的样本量
raw_x = np.sort(6 * np.random.rand(n, 1) - 3, axis=0) # [-3, 3]区间,排序,二维数组n * 1
raw_y = objective_fun(raw_x) + np.random.randn(n, 1) # 二维数组
feature_obj = PolynomialFeatureData(raw_x, degree=13, with_bias=False)
X_train = feature_obj.fit_transform() # 特征数据的构造
X_test_raw = np.linspace(-3, 3, 150) # 测试数据
feature_obj = PolynomialFeatureData(X_test_raw, degree=13, with_bias=False)
X_test = feature_obj.fit_transform() # 特征数据的构造
y_test = objective_fun(X_test_raw) # 测试样本的真值
reg_ratio = [0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5] # 正则化系数
alpha, batch_size, max_epochs = 0.1, 10, 300
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
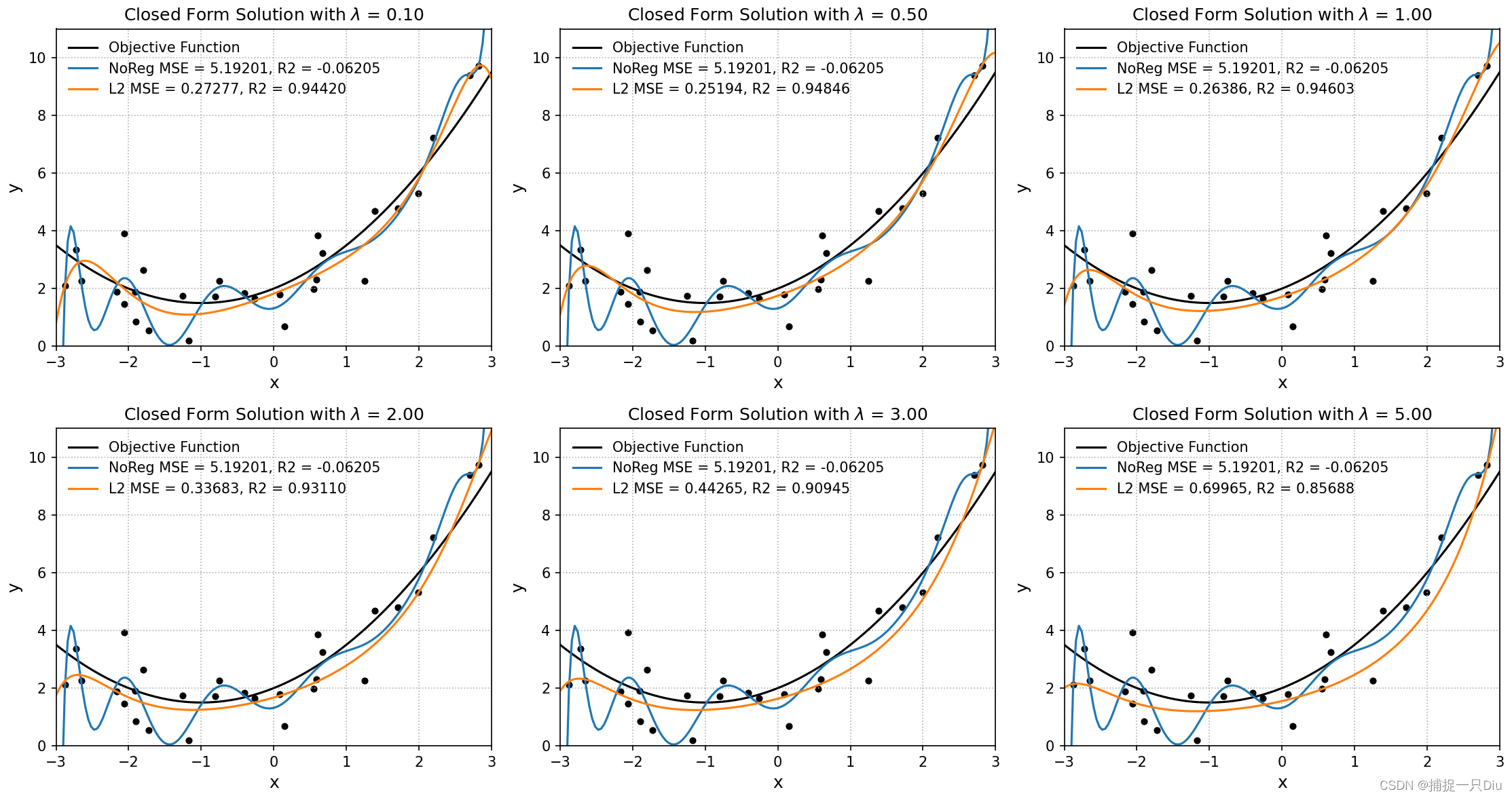
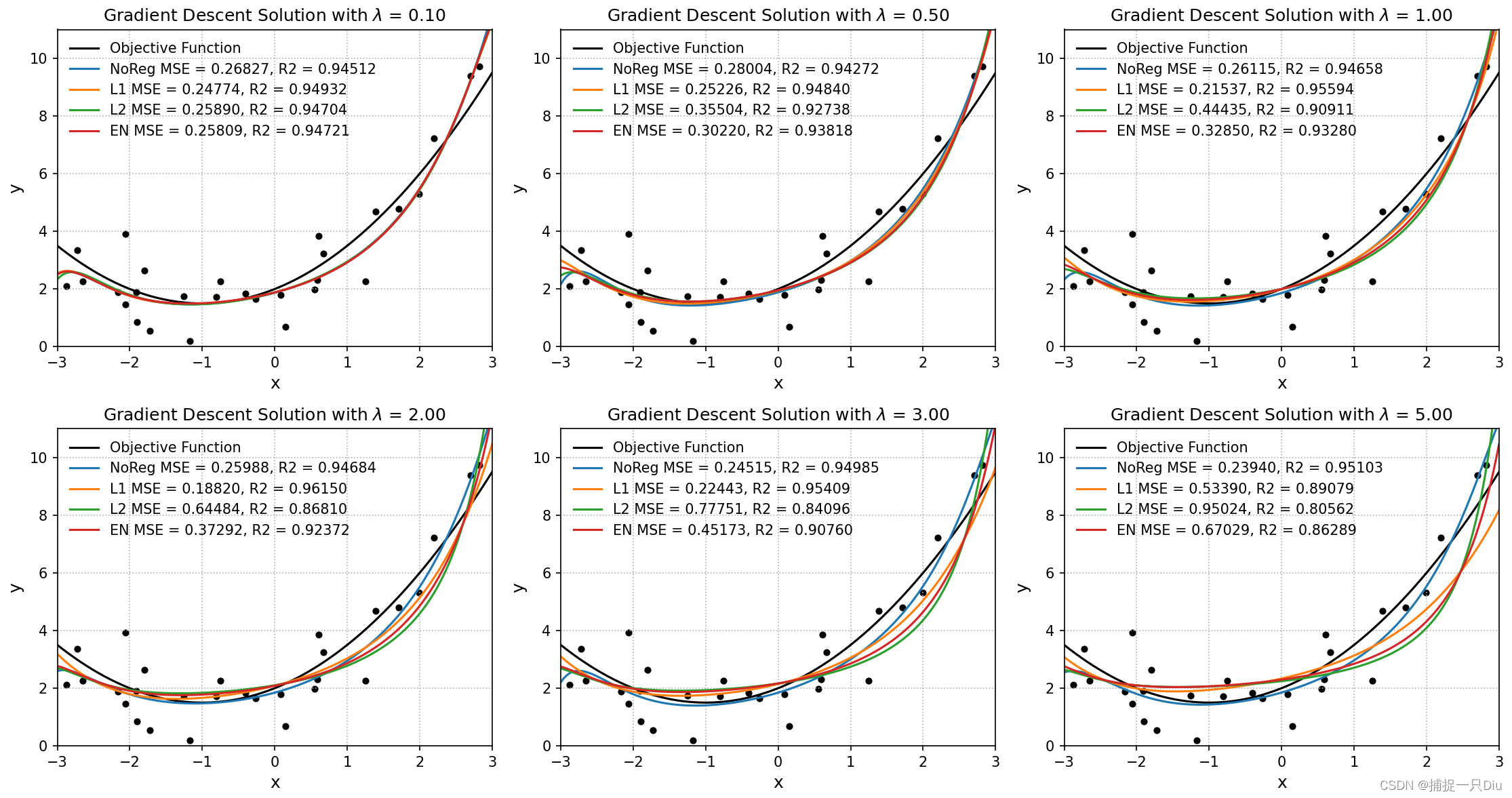
for i, ratio in enumerate(reg_ratio):
plt.subplot(231 + i)
# 不采用正则化
reg_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(solver="grad", alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size,
max_epochs=max_epochs)
reg_lr.fit(X_train, raw_y)
print("NoReg, ratio = 0.00", reg_lr.get_params())
print("=" * 70)
y_test_pred = reg_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
mse, r2, _ = reg_lr.cal_mse_r2(y_test, y_test_pred)
plt.scatter(raw_x, raw_y, s=15, c="k")
plt.plot(X_test_raw, y_test, "k-", lw=1.5, label="Objective Function")
plt.plot(X_test_raw, y_test_pred, lw=1.5, label="NoReg MSE = %.5f, R2 = %.5f" % (mse, r2))
# LASSO回归
# LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator 最小绝对收缩与选择算子
lasso_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(solver="grad", alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size,
max_epochs=max_epochs, l1_ratio=ratio)
lasso_lr.fit(X_train, raw_y)
print("L1, ratio = %.2f" % ratio, lasso_lr.get_params())
print("=" * 70)
y_test_pred = lasso_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
mse, r2, _ = lasso_lr.cal_mse_r2(y_test, y_test_pred)
plt.plot(X_test_raw, y_test_pred, lw=1.5, label="L1 MSE = %.5f, R2 = %.5f" % (mse, r2))
# 岭回归
ridge_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(solver="grad", alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size,
max_epochs=max_epochs, l2_ratio=ratio)
ridge_lr.fit(X_train, raw_y)
print("L2, ratio = %.2f" % ratio, ridge_lr.get_params())
print("=" * 70)
y_test_pred = ridge_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
mse, r2, _ = ridge_lr.cal_mse_r2(y_test, y_test_pred)
plt.plot(X_test_raw, y_test_pred, lw=1.5, label="L2 MSE = %.5f, R2 = %.5f" % (mse, r2))
# 弹性网络回归
elastic_net_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(solver="grad", alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size,
max_epochs=max_epochs, l2_ratio=ratio, l1_ratio=ratio, en_rou=0.5)
elastic_net_lr.fit(X_train, raw_y)
print("EN, ratio = %.2f" % ratio, elastic_net_lr.get_params())
print("=" * 70)
y_test_pred = elastic_net_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
mse, r2, _ = elastic_net_lr.cal_mse_r2(y_test, y_test_pred)
plt.plot(X_test_raw, y_test_pred, lw=1.5, label="EN MSE = %.5f, R2 = %.5f" % (mse, r2))
plt.axis([-3, 3, 0, 11])
plt.xlabel("x", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.ylabel("y", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
plt.legend(frameon=False)
plt.grid(ls=":")
#plt.title("Closed Form Solution with $\lambda$ = %.2f" % ratio)
plt.title("Gradient Descent Solution with $\lambda$ = %.2f" % ratio)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
案例测试
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Bias+correction+of+numerical+prediction+model+temperature+forecast
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from regularization_linear_regression import RegularizationLinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
data = pd.read_csv("bias+correction+of+numerical+prediction+model+temperature+forecast/Bias_correction_ucl.csv").dropna()
X, y = np.asarray(data.iloc[:, 2:-2]), np.asarray(data.iloc[:, -1])
feature_names = data.columns[2:-2]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=22)
alpha, batch_size, max_epochs, ratio = 0.2, 100, 500, 0.5
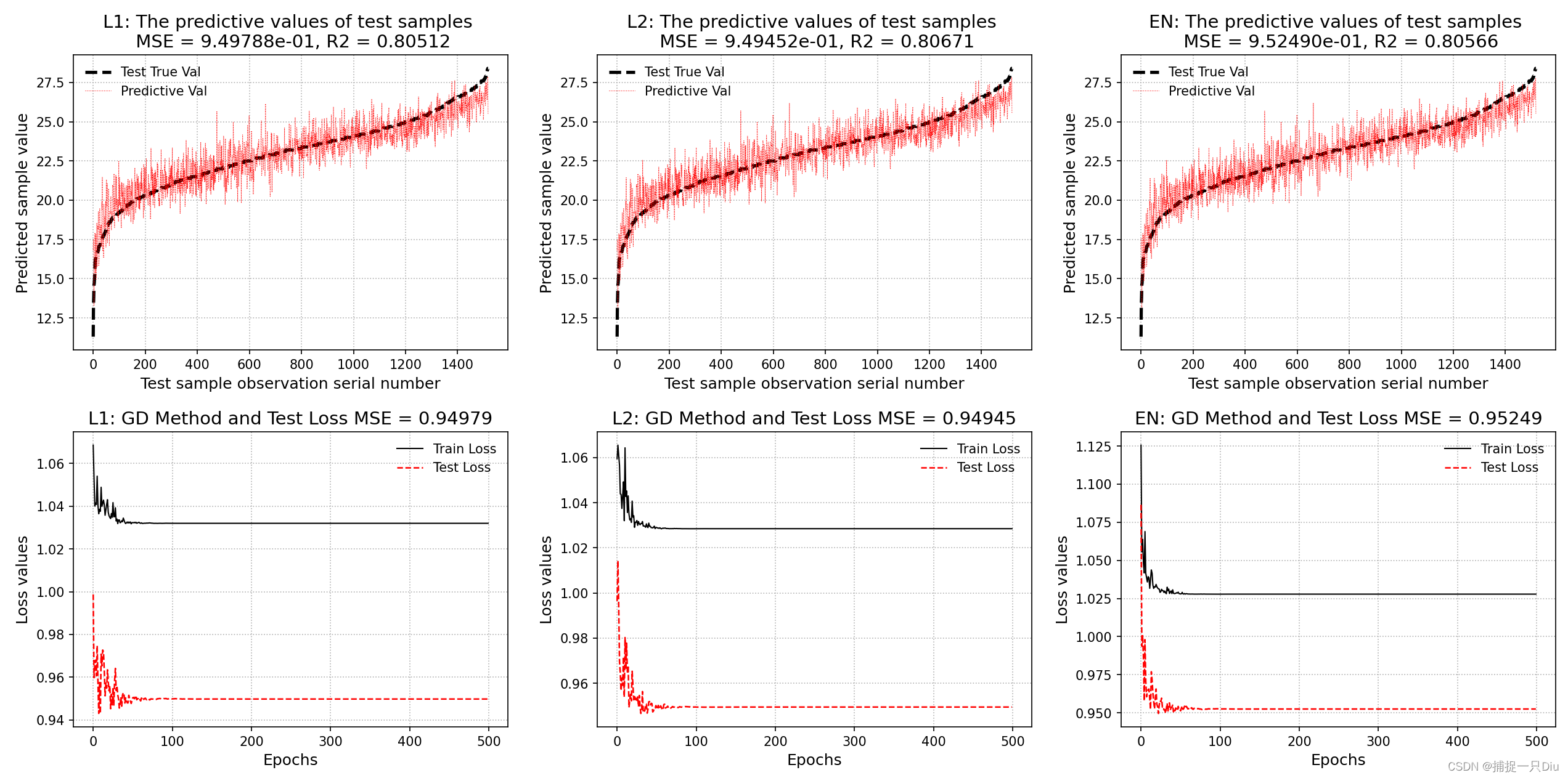
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8))
noreg_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size, max_epochs=max_epochs)
noreg_lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
theta = noreg_lr.get_params()
print("无正则化,模型系数如下")
for i, w in enumerate(theta[0][:-1]):
print(feature_names[i], ":", w)
print("theta0:", theta[1][0])
print("=" * 50)
lasso_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size, max_epochs=max_epochs, l1_ratio=1)
lasso_lr.fit(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test)
theta = lasso_lr.get_params()
print("LASSO正则化,模型系数如下")
for i, w in enumerate(theta[0][:-1]):
print(feature_names[i], ":", w)
print("theta0:", theta[1][0])
print("=" * 50)
plt.subplot(231)
y_test_pred = lasso_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
lasso_lr.plt_predict(y_test, y_test_pred, lab="L1", is_sort=True, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(234)
lasso_lr.plt_loss_curve(lab="L1", is_show=False)
ridge_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size, max_epochs=max_epochs, l1_ratio=ratio)
ridge_lr.fit(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test)
theta = ridge_lr.get_params()
print("岭回归正则化,模型系数如下")
for i, w in enumerate(theta[0][:-1]):
print(feature_names[i], ":", w)
print("theta0:", theta[1][0])
print("=" * 50)
plt.subplot(232)
y_test_pred = ridge_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
ridge_lr.plt_predict(y_test, y_test_pred, lab="L2", is_sort=True, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(235)
ridge_lr.plt_loss_curve(lab="L2", is_show=False)
en_lr = RegularizationLinearRegression(alpha=alpha, batch_size=batch_size, max_epochs=max_epochs,
l1_ratio=ratio, l2_ratio=ratio, en_rou=0.3)
en_lr.fit(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test)
theta = en_lr.get_params()
print("弹性网络正则化,模型系数如下")
for i, w in enumerate(theta[0][:-1]):
print(feature_names[i], ":", w)
print("theta0:", theta[1][0])
print("=" * 50)
plt.subplot(233)
y_test_pred = en_lr.predict(X_test) # 测试样本预测
en_lr.plt_predict(y_test, y_test_pred, lab="EN", is_sort=True, is_show=False)
plt.subplot(236)
en_lr.plt_loss_curve(lab="EN", is_show=False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
猜你喜欢
网友评论
- 搜索
- 最新文章
- 热门文章
